您现在的位置是: 首页 > 文案大全 文案大全
英语句子类型_英语句子类型讲解
tamoadmin 2024-08-15 人已围观
简介1.英语句子四种基本类型2.句子的类型有哪些?快!3.英语里面有几种句子类型4.英语句子的种类和用法,有哪些啊?5.英语句子的基本类型6.英语五个基本句子类型7.英语语法基础:句子的种类一、 主语+系动词(be)+表语句型在这类句型中,谓语动词是系动词(be)的形式,主要有is、am、are、was、were。比如:I am a student and very like English clas
1.英语句子四种基本类型
2.句子的类型有哪些?快!
3.英语里面有几种句子类型
4.英语句子的种类和用法,有哪些啊?
5.英语句子的基本类型
6.英语五个基本句子类型
7.英语语法基础:句子的种类
一、 主语+系动词(be)+表语句型
在这类句型中,谓语动词是系动词(be)的形式,主要有is、am、are、was、were。比如:I am a student and very like English class.我是一个学生非常喜欢英语课。
二、 主语+谓语动词(不及物动词)
在这类句型中,谓语动词是不及物动词,这类动词后面是不可以接宾语的,但是可以接任意性状语。所谓的任意性状语是指去掉后,并不会影响句子完整的结构和意义。比如:The orange was not to keep for a long time.橘子是不好长期保存的。
三、 主语+动词(及物动词)+宾语
在这类句型中,谓语动词是及物动词,而且是只接一个宾语的及物动词,这种动词我们经常称为单宾语及物动词。比如:He had left my home yesterday , he can’t tell you.他昨天已经离开我家了,他没有告诉你。
四、 主语+谓语(及物动词)+间接宾语+直接宾语
在这类句型中,谓语动词是能够接两个宾语的及物动词,我们经常称这类动词为双宾语动词。比如:She give me a new book in my birthday.在我生日上她送给了我一本新书。
五、主语+谓语+宾语+状语
比如:I he left Beijing at five.我在五点就离开了北京。
英语句子四种基本类型
英语五大基本句型 基本概念:与汉语相似,英语句子是由主语(subject), 谓语动词(verb),宾语(object), 表语(predicative),状语(adverbial),宾语补足语(object complement)等成分组成,按照这些成分的组合方式英语句子可分为五种基本句型。 句型一:主语+不及物动词 不及物动词本身就可以表达完整的意念, 不需要宾语及补语, 但有时可有副词, 介词短语等状语修饰语。 e.g. The rain stopped . The old man walks in the park . 句型一的扩展:1.主语+不及物动词+状语 e.g. The machine works smoothly. (机器运转正常。) 2.There +不及物动词+主语 e.g. There is some milk in the bottle . There comes the bus . 3. 主语+不及物动词+ 动词不定式 e.g. They stopped to take a short rest . (他们停下来稍作休息) 特别提醒 动词stop 可用作不及物动词,也可用作及物动词。作不及物动词时, 通常后接动词不定式,表示停下来的目的是做另一件事。作及物动词时,通常后接动名词,表示停止做这件事。 e.g. They stopped taking a rest . 句型二 :主语+系动词+表语 系动词本身不能表达完整的意念没,需要形容词,名词,介词短语等来补充说明主语,也叫主语补语。 e.g. My sister is a nurse . I feel quite hungry . The ball is under the desk . 句型三:主语+及物动词+宾语 及物动词本身需要一个动作的接受者(宾语),才可以表达一个完整的意念。 e.g. We are learning English . Do you know him ? Your radio needs repairing . She hopes to see her uncle. 句型四:主语+及物动词+间接宾语+直接宾语 有些及物动词需要两个宾语才能表达一个完整意念。 e.g. Her mother bought her a skirt. Give me the book, please. 特别提醒 A. 在此句型中, 通常是间接宾语(人)在前,直接宾语(物)在后,有时直接宾语和间接宾语可以对调,这时间接宾语前应加上适当的介词。 e.g. Her mother bought a skirt for her . Give the book to me , please . 直接宾语与间接宾语对调时,间接宾语前加介词to的动词有: give(给), tell(告诉) , lend(借给) , sell(卖), teach(教) , send(寄给), write(写给), show(出示) , return(还给), bring(带给), pass(递给), lee(留给), offer(提供), hand(交给) 间接宾语前加介词for的动词有: buy(买), choose(选择), get (弄到), make(做), order(订购), sing (唱歌), do (做), play(演奏) B. 如果直接宾语为人称代词那么必须把直接宾放在间接宾语前,且间接宾语前要加上适当的介词。 e.g. I handed it to our teacher . 不能说:I handed our teacher it . C. 此句型变为被动语态时,可分为两种情况。 e.g. Her mother bought her a skirt . a. She was bought a skirt by her mother . b. A skirt was bought for her by her mother. 句型五:主语+及物动词+宾语+宾语补足语 及物动词本身需要一个宾语外, 还需要一个名词,形容词,副词, 动词不定式,分词来补充说明宾语,才能表达一个完整的意念。 e.g. We elected Li Yang our monitor. The news made us sad. She saw the thief steal into the shop . The teacher asked me to answer the question . I found the man stealing the money . I found my money stolen . 特别提醒 A. 现在分词为宾语补足语时,宾语与现在分词之间是主动关系;过去分词为宾语补足语时,宾语与过去分词之间是被动关系。 B. 在let(让),make(使得),he(请,让,使得),see(看),hear(听到),watch(观看),feel(感觉到),listen to (倾听),look at (看到),notice(注意到)等动词后的宾语补足语如果为不定式, 则省掉”to”,但变为被动语态时, 则要带”to”. e.g. We hear her sing next door. She is heard to sing next door . C. 此句型变为被动语态时,只有一种情况。 e.g. They saw him steal the old man’s money.
满意请纳
句子的类型有哪些?快!
一,简单句(simple sentence)
简单句只由一个独立子句构成,它至少包含一个主语和一个动词。它还可以包含宾语和修饰词。
例句:
Birds fly.
Studies serve for delight, for ornament, and for ability.
二,复合句(compound sentence)
复合句由至少两个独立子句构成,中间由连接词构成,也可以由分号、冒号、破折号连接。
连接词包括:
Only two things are infinite, the universe and human stupidity,?and?I'm not sure about the former.
三,复杂句(complex sentence)
复杂句由一个独立子句以及至少一个从属子句构成,它们之间由连词连接。
在复杂句中,从属子句往往是对独立子句起到一个解释说明的作用,告诉读者更多的信息。它或是表现出一种因果关系,或是表现在时间或者空间上的关系。
四,复合复杂句(compound-complex sentence)
复合复杂句由至少两个独立子句和至少一个从属子句构成,子句和子句之间用连接词相连。
例句:
(黑体部份为两个独立子句,斜体部份为从属子句。)
Kate doesn’t like cartoons?because they are loud,?so she?doesn’t watch them.
The cat jumped onto the couch?and?sat down on top of the remote control?just when I was reaching for it.
英语里面有几种句子类型
在英语当中句子按其用途可分为四个种类:
1)陈述句(declarative sentence),用以陈述事实.
例如:I don't care what she thinks.(我不在乎她想什么.)
2)疑问句(interrogative sentence),用以提出问题.
例如:When do we meet again?(我们什么时候再见面.)
3)祈使句(imperative sentence),用以表示命令,请求等.
例如:Let the meat cook slowly.(把肉用文火煮.)
4)感叹句(exclamatory sentence),用以表示各种强烈的感情.
例如:The noise will deafen us all!(这噪音会使我们大家耳聋的!)
英语句子的种类和用法,有哪些啊?
1简单句、并列句、复合句
根据语法形式,即句子的结构,英语的句子可分为简单句、并列句和复合句。
1简单句
句型:主语+谓语
只包含一个主谓结构,而句子的各个结构都只由单词或短语表示。简单句有五种基本句型,详见第十七章。
They are playing baseball in the garden.
他们正在公园里打棒球。
Her brother and sister both are teachers.
她的哥哥和姐姐都是老师。
2并列句
句型:简单句+并列连词+简单句
(常见的并列连词有and,but,or)
并列句是由两个或两个以上的简单句连接而成。并列句中的各简单句意义同等重要,相互之间没有从属关系,是平行并列的关系。它们之间用连词连结。
My friend was at home, and we talked for along time.
我的朋友在家,我们谈了好长时间。
Her father is a doctor and her mother is a teacher.
她父亲是个医生,她母亲是个老师。
I liked the story very much but Li Ming wasn't interested in it.
我非常喜欢这个故事,可是李明却对它不感兴趣。
Hurry up,or you'll be late.
快点,否则你就会迟到的。
3 复合句
句型:主句+连词+从句;或连词+从句+主句(包含一个主句、一个或一个以上的从句,或只包含一个从句,但有两个或两个以上的主句的句子叫复合句。)
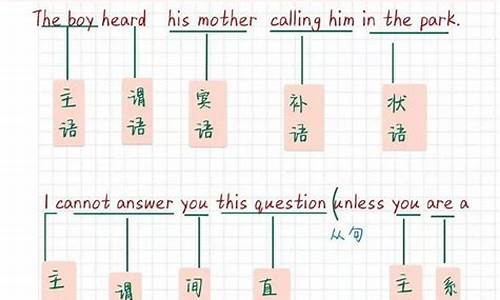
句子的成分
组成句子的各个部分叫做句子的成分。句子成分包括:主语、谓语、表语、宾语(直接宾语、间接宾语)、宾语补足语、定语和状语。主语和谓语是句子主体部分(在英文中一般的句子必须有主语和谓语)。表语、宾语和宾语补足语是谓语里的组成部分。其他成分如定语和状语是句子的次要部分。下面我们分别讲述一下句子的各个成分:
1 主语
主语是谓语讲述的对象,表示所说的“是什么”或“是谁”。一般由名词、代词、不定式或相当于名词的词或短语来充当。它在句首。
We study in No.1 Middle School.(讲述“谁”~)
我们在一中学习。
The classroom is very clean.
(讲述“什么”很干净)
这间教室很干净。
Three were absent.(数词作主语)
三个人缺席。
To teach them English is my job.
(不定式作主语)
教他们英语是我的工作。
注意
不定式作主语时,常用形式主语it句型,因此左例可变为It is my job to teach them English.
(真正的主语是to teach them English.)
2 谓语
说明主语“做什么”,“是什么”或“怎么样”。
谓语(谓语部分里主要的词)必须用动词。谓语和主语在人称和数两方面必须一致。它在主语后面。
His Parents are doctors.
(系动词和表语一起作谓语)
他的父母亲是医生。
She looks well.(系动词和表语一起作谓语)
她看起来气色(面色)很好。
We study hard.(实义动词作谓语)
我们努力学习。
We he finished reading the book.
(助动词和实义动词一起作谓语)
我们已经看完了这本书。
He can speak English.
(情态动词和实义动词作谓语)
他会说英语。
3 表语
表语说明主语“是什么”或者“怎么样”,由名词、形容词、副词、介词、不定式及相当于名词或形容词的词或短语来担任。它的位置在系动词后面。
You look younger than before.(形容词作表语)
你看起来比以前年轻。
I am a teacher.(名词作表语)
我是个老师。
Everybody is here.(副词作表语)
所有的人都出席了。
They are at home now.(介词短语作表语)
他们现在在家。
My job is to teach them English.(不定式作表语)
我的工作是教他们英语。
4 宾语
宾语是动作、行为的对象,由名词、代词、不定式或相当于名词的词、短语来担任,它和及物动词一起说明主语做什么,在谓语之后。(直接宾语、间接宾语详见后面五种基本句型)。
She is playing the piano now.(名词作宾语)
她正在弹钢琴。
He often helps me.(代词作宾语)
他常常帮助我。
He likes to sleep in the open air.(不定式作宾语)
他喜欢在露天睡觉。
We enjoy living in China.(动名词作宾语)
我们高兴住在中国。
5状语
状语用来修饰动词、形容词或副词。一般表示行为发生的时间、地点、目的、方式、程度等意义,一般由副词、介词短语、不定式或相当于副词的词或短语来表示。状语一般放在句末,但有的可以放在句首、句中。(详见副词)
He did it carefully.(副词作状语)
他仔细、认真地做这项工作。
Without his help,we couldn't work it out.
(介词短语作状语)
如果没有他的帮助,我们不可能解决这个问题。
(In order) to catch up with my classmates, I must study hard.(不定式作目的状语)
为了赶上我的同学,我必须努力学习。
6 定语
英语句子的基本类型
一、陈述句:是用来陈述一件事情或表示一种看法,可分为肯定句和否定句两种形式。
1、谓语动词是be动词,助动词he, has, will,情态动词can等时,只要直接在这些词后面加not就构成否定形式。
eg. Lily has already read this new book. (改为否定句)
Lily ______ ______ this new book ________.
2、谓语动词是行为动词而又没有助动词或情态动词时,必须在谓语动词前加助动词,一般现在时加助动词do ,第三人称单数加does,一般过去时加did,再和not构成否定结构。必须指出的是:don't, doesn't, didn't后都用动词原形。
eg.1)Jill has lunch at school every day. (改为否定句)
Jill _____ _____ lunch at school every day.
2)The children had a good time at the party. (改为否定句)
The children ______ _____ a good time at the party.
3)Rose didn't drink any milk this morning.(改为肯定句)
Rose ______ ______ milk this morning.
二、疑问句:是用来提出问题的句子。
A.一般疑问句:以be动词, he /has/do等助动词、can/may等情态动词开头,以yes或no来回答的问句。
它的基本结构是:Be/He /Has/Did等助动词(包括情态动词)+主语+谓语(包括表语)+┄?回答常用简略回答。
1、谓语动词是be动词、助动词、情态动词时,只要直接把这些词置于句首,句末改成问号。
eg. There's something wrong with his bike.(改成疑问句)
______ _____ _______ wrong with his bike?
2、谓语动词是行为动词时,必须在句首加上助动词Do、Does(三单)、Did(过去式)加上这些助动词后,句子中谓语动词必须用原形。
eg. 1)Edison built a science lab himself when he was ten. (改成疑问句)
______ Edison ______ a science lab himself when he was ten?
2)Those Japanese like Chinese food.(改成疑问句)
______ those Japanese ________ Chinese food?
注意:在把肯定句改成否定句或一般疑问句的时候,要注意句中是否有already、some、something、somebody等词,如果有也必须进行改变,already要改成yet,some、something、somebody等分别改成any、anything、anybody等。另外,在改成否定句的时候注意把too改成either,both改成neither,all改成none等.在改成一般疑问句的时候,常常把第一人称I、we改成第二人称you。
B.特殊疑问句:以疑问代词或疑问副词开头,提出疑问的句子。
它的基本结构是:特殊疑问词+一般疑问句语序。但是如果疑问词在句子中作主语或作主语的定语,就用特殊疑问词+陈述句语序。常用的疑问词有:what, who(whom), whose,which,when,where,how,why等,回答时针对问句中的代词和副词来回答,不用yes或no来回答。
1)对指物名词或谓语动词提出疑问,疑问词用what
①The twins were making a kite when their mother came in. (划线提问)
______ _____ the twins _____ when their mother came in?
②Mrs Turner asked her son to buy some eggs for supper. (划线提问)
_______ ______ Mrs Turner ask her son ______ _______?
2)对名词前定语提出疑问,疑问词应用which,而且必须和名词连用。
I'm going to take the shirt on the right.(划线提问)
______ _____ are you going to take?
3)对指人名词或代词提问用who,作宾语时提问用whom。
eg.Li Ping,they,his father
4)对物主代词和名词所有格提问用whose。
eg. Li Ping's coat→Whose coat my father→Whose father
5)对具体时间提出疑问,如 in the morning,last Sunday等,疑问词用when;对具体几点钟提问,疑问词应用what time。
6)对具体地点提出疑问,疑问词应用where。
The pupils are hing a picnic at the foot of the hill. (划线提问)
_____ _____ the pupils hing a picnic?
7)对表原因的从句提问,常见的有because引导的从句,疑问词应用why。
Xiao Cheng didn't go to the farm with us because he was ill. (划线提问)
_______ _____ Xiao Cheng go to the farm with us?
8)对方式或程度等提出疑问,用疑问词How。
eg. go by bike like very much
9)对数量提出疑问,疑问词为How many,要注意how many必须跟名词的复数形式。
eg. two hundred sheep→How many sheep
10)对价格提出疑问,疑问词用How much。
eg. I paid fifty yuan for the sweater.
______ ______ did you pay for the sweater?
11)对时间长度提出疑问,疑问词应用How long。
eg. I've worked in that factory for two years. (划线提问)96中考题
______ _____ _______ you worked in that factory?
12)对时间频率,如 once a year, twice a week等提问,疑问词用How often。
13)对具体次数,如 once, twice, three times等提问,疑问词用How many times。
eg. ______ did he call you the day before yesterday?Twice. 96中考题
A.What time B.How many times C.How much D.How long
14)对in+一段时间提问,疑问词一般用How soon。
eg. Jane and her brother will finish the work in two hours. (划线提问)
_____ _____ _____ Jane and her brother finish the work?
15)对距离提出疑问,疑问词用How far。
eg. It's about two kilometres from here to the country.(划线提问)
______ _____ _____ _____ from here to the country?
16)另外,对日期、星期、天气等提出疑问,则分别用
What's the date?
What day is it ? 如果是过去时间,就用was代替is。
What's the weather like?
练习题
1)She does exercises at home in the evening.(改成否定句、一般疑问句)
She ______ ______ exercises at home in the evening.
______ she _____ exercises at home in the evening?
2)He said something important at the meeting.(改为否定句,一般疑问句)
He _____ ______ ______ important at the meeting.
______ he ______ ______ important at the meeting?
3)It'll take them three weeks to finish the work.(划线提问)
______ ______ _______ it take them to finish the work?
4)I he to wash all the plates and things after meals.(划线提问)
_____ _____ you he to wash all the plates and things?
5)The woman in the red coat is her mother.(划线提问)
______ ______ is her mother?
6)Li Ping spent twenty yuan on the dictionary.(划线提问)
_____ ____ ____ Li Ping _____ on the dictionary?
思考题
1)The worker's visited the factory already.(改成否定句、一般疑问句)
The worker _____ _____ the factory ______.
____ the worker ___ the factory __?
2)Both of his parents are workers.(改成否定句)
___ of his parents ______ a worker.
3)He went to the park with his sister.(划线提问)
_____ ____ ____ he go to the park?
4)We really enjoyed working on the farm.(划线提问)
What _____ you really enjoy ______?
5)She writes to her parents once a week.(划线提问)
_______ ______ ______ she write to her parents?
6)Our P.E teacher has been at this school since he came.(划线提问)
______ ______ ______ our P.E teacher been at this school?
一、陈述句:是用来陈述一件事情或表示一种看法,可分为肯定句和否定句两种形式。
1、谓语动词是be动词,助动词he, has, will,情态动词can等时,只要直接在这些词后面加not就构成否定形式。
eg. Lily has already read this new book. (改为否定句)
Lily ______ ______ this new book ________.
2、谓语动词是行为动词而又没有助动词或情态动词时,必须在谓语动词前加助动词,一般现在时加助动词do ,第三人称单数加does,一般过去时加did,再和not构成否定结构。必须指出的是:don't, doesn't, didn't后都用动词原形。
eg.1)Jill has lunch at school every day. (改为否定句)
Jill _____ _____ lunch at school every day.
2)The children had a good time at the party. (改为否定句)
The children ______ _____ a good time at the party.
3)Rose didn't drink any milk this morning.(改为肯定句)
Rose ______ ______ milk this morning.
二、疑问句:是用来提出问题的句子。
A.一般疑问句:以be动词, he /has/do等助动词、can/may等情态动词开头,以yes或no来回答的问句。
它的基本结构是:Be/He /Has/Did等助动词(包括情态动词)+主语+谓语(包括表语)+┄?回答常用简略回答。
1、谓语动词是be动词、助动词、情态动词时,只要直接把这些词置于句首,句末改成问号。
eg. There's something wrong with his bike.(改成疑问句)
______ _____ _______ wrong with his bike?
2、谓语动词是行为动词时,必须在句首加上助动词Do、Does(三单)、Did(过去式)加上这些助动词后,句子中谓语动词必须用原形。
eg. 1)Edison built a science lab himself when he was ten. (改成疑问句)
______ Edison ______ a science lab himself when he was ten?
2)Those Japanese like Chinese food.(改成疑问句)
______ those Japanese ________ Chinese food?
注意:在把肯定句改成否定句或一般疑问句的时候,要注意句中是否有already、some、something、somebody等词,如果有也必须进行改变,already要改成yet,some、something、somebody等分别改成any、anything、anybody等。另外,在改成否定句的时候注意把too改成either,both改成neither,all改成none等.在改成一般疑问句的时候,常常把第一人称I、we改成第二人称you。
B.特殊疑问句:以疑问代词或疑问副词开头,提出疑问的句子。
它的基本结构是:特殊疑问词+一般疑问句语序。但是如果疑问词在句子中作主语或作主语的定语,就用特殊疑问词+陈述句语序。常用的疑问词有:what, who(whom), whose,which,when,where,how,why等,回答时针对问句中的代词和副词来回答,不用yes或no来回答。
1)对指物名词或谓语动词提出疑问,疑问词用what
①The twins were making a kite when their mother came in. (划线提问)
______ _____ the twins _____ when their mother came in?
②Mrs Turner asked her son to buy some eggs for supper. (划线提问)
_______ ______ Mrs Turner ask her son ______ _______?
2)对名词前定语提出疑问,疑问词应用which,而且必须和名词连用。
I'm going to take the shirt on the right.(划线提问)
______ _____ are you going to take?
3)对指人名词或代词提问用who,作宾语时提问用whom。
eg.Li Ping,they,his father
4)对物主代词和名词所有格提问用whose。
eg. Li Ping's coat→Whose coat my father→Whose father
5)对具体时间提出疑问,如 in the morning,last Sunday等,疑问词用when;对具体几点钟提问,疑问词应用what time。
6)对具体地点提出疑问,疑问词应用where。
The pupils are hing a picnic at the foot of the hill. (划线提问)
_____ _____ the pupils hing a picnic?
7)对表原因的从句提问,常见的有because引导的从句,疑问词应用why。
Xiao Cheng didn't go to the farm with us because he was ill. (划线提问)
_______ _____ Xiao Cheng go to the farm with us?
8)对方式或程度等提出疑问,用疑问词How。
eg. go by bike like very much
9)对数量提出疑问,疑问词为How many,要注意how many必须跟名词的复数形式。
eg. two hundred sheep→How many sheep
10)对价格提出疑问,疑问词用How much。
eg. I paid fifty yuan for the sweater.
______ ______ did you pay for the sweater?
11)对时间长度提出疑问,疑问词应用How long。
eg. I've worked in that factory for two years. (划线提问)96中考题
______ _____ _______ you worked in that factory?
12)对时间频率,如 once a year, twice a week等提问,疑问词用How often。
13)对具体次数,如 once, twice, three times等提问,疑问词用How many times。
eg. ______ did he call you the day before yesterday?Twice. 96中考题
A.What time B.How many times C.How much D.How long
14)对in+一段时间提问,疑问词一般用How soon。
eg. Jane and her brother will finish the work in two hours. (划线提问)
_____ _____ _____ Jane and her brother finish the work?
15)对距离提出疑问,疑问词用How far。
eg. It's about two kilometres from here to the country.(划线提问)
______ _____ _____ _____ from here to the country?
16)另外,对日期、星期、天气等提出疑问,则分别用
What's the date?
What day is it ? 如果是过去时间,就用was代替is。
What's the weather like?
练习题
1)She does exercises at home in the evening.(改成否定句、一般疑问句)
She ______ ______ exercises at home in the evening.
______ she _____ exercises at home in the evening?
2)He said something important at the meeting.(改为否定句,一般疑问句)
He _____ ______ ______ important at the meeting.
______ he ______ ______ important at the meeting?
3)It'll take them three weeks to finish the work.(划线提问)
______ ______ _______ it take them to finish the work?
4)I he to wash all the plates and things after meals.(划线提问)
_____ _____ you he to wash all the plates and things?
5)The woman in the red coat is her mother.(划线提问)
______ ______ is her mother?
6)Li Ping spent twenty yuan on the dictionary.(划线提问)
_____ ____ ____ Li Ping _____ on the dictionary?
思考题
1)The worker's visited the factory already.(改成否定句、一般疑问句)
The worker _____ _____ the factory ______.
____ the worker ___ the factory __?
2)Both of his parents are workers.(改成否定句)
___ of his parents ______ a worker.
3)He went to the park with his sister.(划线提问)
_____ ____ ____ he go to the park?
4)We really enjoyed working on the farm.(划线提问)
What _____ you really enjoy ______?
5)She writes to her parents once a week.(划线提问)
_______ ______ ______ she write to her parents?
6)Our P.E teacher has been at this school since he came.(划线提问)
______ ______ ______ our P.E teacher been at this school?
句型转换题是中考常见题型,它主要用来考查大家对句子结构的构成、变化的掌握及在行文中的运用等,类型繁多。现以近两年中考题为例,分类介绍如下:
[第一类] 改成否定句
英语中有关否定的结构各不相同,除动词部分构成的否定外,还有名词、代词的否定、部分否定、否定转移、以及一些表示否定意义的短语或句型等。
一、含有连系动词、情态动词等助动词的句子改为否定句时,在连系动词、情态动词等的后面加not就行了。如:(划线部分为正确答案,下同。)
1. He was late for school yesterday. (2005黑龙江省泰州市)
He wasn’t late for school yesterday.
2. The students of No.2 Middle School he gone for a picnic already. (2004新疆)
The students of No.2 Middle School hen’t gone for a picnic yet.
二、祈使句变否定句一般在其前加don’t。如:
3. Open the window. (2005江苏省)
Don’t open the window.
三、实义动词的否定式是在实义动词前加don’t, doesn’t, didn’t等。如:
4. She does the housework every day. (2005黑龙江省哈尔滨市)
She doesn’t do the housework every day.
5. He returned the book to the library this morning. (2004重庆市)
He didn’t return the book to the library this morning.
注意:变否定句时须注意某些词语的变化,如some改为any, something改为anything, already改为yet, both改为neither, all改为none等。又如:
6. Both of them are my best friends. (2004甘肃省兰州市)
Neither of them is my best friend.
[第二类] 改为疑问句
可分为一般疑问句、选择疑问句和反意疑问句。
一、变一般疑问句时,含有连系动词、情态动词的句子,只需将它们移至句首,第一个字母变为大写,句尾改为问号即可。含有实义动词的句子,在实义动词前加do, does, did等。变化过程中也要注意某些词语和人称的变化。如:
7. There’s something to eat in the cupboard.(2005贵州省贵阳市)
Is there anything to eat in the cupboard?
8. Kate does morning exercises every day. (2004山东省济南市)
Does Kate do morning exercises every day?
9. Ann returned the book to the library yesterday. (2005四川省成都市)
Did Ann return the book to the library yesterday?
二、变选择疑问句时,如果该句是一般疑问句,则在后面直接加“or+另一选择部分”就行了;若是陈述句,则要先变成一般疑问句。如:
10. John is an American. (用a Canadian改为选择疑问句)(2004新疆)
Is John an American or a Canadian?
三、变反意疑问句时,要注意“前肯后否”和“前否后肯”,还要注意一些特殊形式的反意疑问句。如:
11. She has hardly had anything this morning, has she?(2005山东省泰安市)
12. You will meet your friends at the railway station, won’t you?(2004重庆)
13. She had nothing for breakfast, did she?(2005青海)
14. There was no time for the twins to go shopping, was there?(2004黑龙江省哈尔滨市)
英语五个基本句子类型
英语句子的基本类型:主+谓;主+谓+表;主+谓+宾;主+谓+间宾+直宾;主+谓+宾+宾补。
1、主+谓。句子的谓语动词都能表达完整的意思。这类动词叫做不及物动词,后面可以跟副词、介词短语、状语从句等。
2、主+谓+表。句子谓语动词都不能表达一个完整的意思,必须加上一个表明主语身份或状态的表语构成复合谓语,才能表达完整的意思。这类动词叫做连系动词。
3、主+谓+宾。谓语动词都具有实义,都是主语产生的动作,但不能表达完整的意思,必须跟有一个宾语,即动作的承受者,才能使意思完整。这类动词叫做及物动词。宾语位于及物动词之后,一般同主语构成一样,不同的是构成宾语的代词必须是‘代词宾格’。
4、主+谓+间宾+直宾。有些及物动词可以有两个宾语,这两个宾语通常一个指人,为间接宾语;一个指物,为直接宾语。间接宾语一般位于直接宾语之前。一般的顺序为:动词+间接宾语+直接宾语;强调间接宾语顺序为:动词+直接宾语+介词+间接宾语;若直接宾语为人称代词:动词+代词直接宾语+介词+ 间接宾语。
5、主+谓+宾+宾补。动词虽然是及物动词,但是只跟一个宾语还不能表达完整的意思,必须加上一个补充成分来补足宾语,才能使意思完整。
英语经典句子
1、What this era lacks is not the person who is perfect but the person who is with virtue, justice, courage and compassion.
2、You whined that she didn’t tell you the truth but did you give her the strength to be truthful to you?
英语语法基础:句子的种类
一、句型1: Subject (主语) + Verb (谓语)
这种句型中的动词大多是不及物动词,所谓不及物动词,就是这种动词后不可以直接接宾语。
二、句型2:Subject (主语) + Link. V(系动词) + Predicate(表语)
这种句型主要用来表示主语的特点、身份等。
三、句型3:Subject(主语) + Verb (谓语) + Object (宾语)
这种句型中的动词一般为及物动词, 所谓及物动词,就是这种动词后可以直接接宾语,其宾语通常由名词、代词、动词不定式、动名词或从句等来充当。
四、句型4: Subject(主语)+Verb(谓语)+ Indirect object(间接宾语)+Direct object (直接宾语)
这种句型中,直接宾语为主要宾语,表示动作是对谁做的或为谁做的,在句中不可或缺,常常由表示“物”的名词来充当;间接宾语也被称之为第二宾语,去掉之后,对整个句子的影响不大,多由指“人”的名词或代词承担。
五、句型5: Subject(主语)+Verb (动词)+Object (宾语)+Complement(补语)
这种句型中的“宾语 + 补语”统称为“复合宾语”。宾语补足语的'主要作用或者是补充、说明宾语的特点、身份等;或者表示让宾语去完成的动作等。担任补语的常常是名词、形容词、副词、介词短语、分词、动词不定式等。
英语语法基础:句子的种类
句子的种类知识是我们学习英语所必须了解的,下面我给大家整理了英语语法基础:句子的种类,欢迎阅读!
英语语法基础:句子的种类
按使用目的可分为陈述句、疑问句、祈使句和感叹句。
1) 陈述句:说明一个事实或陈述一种看法。
Light trels faster than sound. 光比声速度快。
The film is rather boring. 这部**很乏味。
2) 疑问句:提出问题。有以下四种:
a. 一般疑问句:
Can you finish the work in time?
你能按时完成工作吗?
b. 特殊疑问句:
Where do you live? 你住那儿?
How do you know that? 你怎么知道那件事?
c. 选择疑问句:
Do you want tea or coffee?
你是要茶还是要咖啡?
d. 反意疑问句:
He doesnt know her, does he?
他不认识她,对不对?
3) 祈使句:提出请求,建议或发出命令,例如:
Sit down, please. 请坐。
Dont be nervous! 别紧张!
4) 感叹句:表示说话人惊奇、喜悦、愤怒等情绪,例如:
What good news it is! 多好的消息啊!
句子按其结构可以分为以下三类:
1) 简单句:只包含一个主谓结构句子叫简单句,例如:
She is fond of collecting stamps. 她喜欢集邮。
2) 并列句:包含两个或两个以上主谓结构的句子叫并列句,句与句之间通常用并列连词或分号来连接,例如:
The food was good, but he had little etite.
食物很精美,但他却没什么胃口。
3) 复合句:包含一个主句从句和一个或几个从句的句子叫复合句,从句由从属连词引导,例如:
The film had begun when we got to the cinema.
主句从句
我们到达**院的.时候,**已经开演了。
基本句型:英语中千变万化的句子归根结底都是由以下五种基本句型组合、扩展、变化而来的:
1)主 + 动例如:
I work. 我工作。
2)主 + 动 + 表例如:
John is busy. 约翰忙。
3)主 + 动 + 宾例如:
She studies English. 她学英语。
4)主 + 动 + 宾 + 补例如:
Time would prove me right. 时间会证明我是对的。
5)主 + 动 + 间宾 + 直宾例如:
My mother made me a new dress. 我母亲给我做了一件新衣裳。
1 祈使句结构
祈使句用以表达命令,要求,请求,劝告等。
1) 祈使句有两种类型,一种是以动词原形开头,在动词原形之前加do 。
Take this seat.
Do be careful.
否定结构:
Dont move.
Dont be late.
2) 第二种祈使句以let开头。
Let 的反意疑问句
a. Lets 包括说话者
Lets he another try,shall we / shant we?
= Shall we he another try?
b. Let us 不包括说话者
Let us he another try,will you / wont you?
= Will you please let us he another try?
否定结构:
Lets not talk of that matter.
Let us not talk of that matter.
2 感叹句结构
感叹句通常有what, how引导,表示赞美、惊叹、喜 悦、等感情。what修饰名词,how修饰形容词,副词或动词,感叹句结构主要有以下几种:掌握它的搭配,即掌握了感叹句的重点。
How +形容词+ a +名词+ 陈述语序
How+形容词或副词+ 陈述语序
What +名词+ 陈述语序
What+a+形容词+名词+ 陈述语序
What+ 形容词+复数名词+ 陈述语序
What+ 形容词+不可数名词+ 陈述语序
How clever a boy he is!
How lovely the baby is!
What noise they are making!
What a clever boy he is!
What wonderful ideas !
What cold weather it is!
感叹句的省略形式为:
What a clever boy !
两个学生在看书学习
典型例题
1)___ food youve cooked!
A. How a nice B. What a nice C. How nice D. What nice
答案D. 由于How 修饰形容词,副词;what修饰名词。且food为不可数名词,因此A,B 排
除。C How + adj. 后面不能再加名词,因此只有D正确,其句型为What + adj. +n.
2)___terrible weather weve been hing these days!
A. What B. What a C. How D. How a
答案A. weather为不可数名词,B,D排除。C为how + adj. 后面不应有名词。只有A,符
合句型What +形容词+不可数名词。
3) --- _____ I had!
--- You really suffered a lot.
A. What a time B. What time C. How a time D. how time
答案A. 感叹句分两类:
1:What + n.+主谓部分
2:How + adj. / adv. / v.+主谓部分。本题属第一种,但省略了bad,相对于 What a bad
time I had! 这是个习惯用语。
;上一篇:教师名人名言_教师名人名言大全
下一篇:龙族比较经典的话_龙族最燃的句子









