您现在的位置是: 首页 > 经典语录 经典语录
怎么判断英语句型_如何判断英语句子的类型
tamoadmin 2024-08-13 人已围观
简介1.怎样快速地判断出一个英语句子的句式2.英语中句子类型有哪四种3.英语句子成分应当如何判断?高中常见句式结构及其用法4.英语句子的类型有哪些?5.英语句子的种类和用法,有哪些啊?6.英语初中相关语法知识 句子成分主要是怎么判断的 都有哪些固定短语 特殊疑问句一般疑问句如何区分自己的经验哟,帮你整理一下:一般有简单句、复合句、并列句。简单句又分为五类:主谓,主谓宾,主系表,主谓宾宾补,主谓间宾直宾
1.怎样快速地判断出一个英语句子的句式
2.英语中句子类型有哪四种
3.英语句子成分应当如何判断?高中常见句式结构及其用法
4.英语句子的类型有哪些?
5.英语句子的种类和用法,有哪些啊?
6.英语初中相关语法知识 句子成分主要是怎么判断的 都有哪些固定短语 特殊疑问句一般疑问句如何区分
自己的经验哟,帮你整理一下:
一般有简单句、复合句、并列句。
简单句又分为五类:
主谓,主谓宾,主系表,主谓宾宾补,主谓间宾直宾
复合句:也就是简单句的某个成分变成丛句了。
是由主句+从句构成,它是英语中比较复杂的句子结构。一般来说,英语中一个句子只能有一个谓语,如果出现两个谓语动词,那么其中一个谓语动词只能以从句的形式或并列句或非谓语动词的形式出现。所谓从句是指从属于主句的句子,由从属连词连接。从句的种类有很多,但根据其性质和作用可以分为:名词性从句,形容词性从句(即定语从句),副词性从句(即状语从句)三大类
并列句 :也就是几个简单句或复合句搞在一起
由连接词或 " ; "把两个以上(含两个)的简单句连在一起的句子叫做并列句。在并列句中,各个简单句意思完整,不受其他简单句的影响。
These flowers are white and those flowers are red。
这些花是白色的而那些花是红色的。
怎样快速地判断出一个英语句子的句式
判断句,是根据谓语的性质给句子分类得出的一种句型,一般是用名词或名词性词组作谓语,对事物的属性作出判断,即说明某事物是什么,或不是什么。
判断句型
1) 一般判断句
It is important for us to learn English.
It is kind of you to help me
sincere means honest.
The boy is called/named Tom.
We regarded/consider it as an honor.
2)强调判断
It is English that we should learn.
It is he who helped me a lot.
3)弱式判断
Your sentence doesn't sound/look/ear/feel right.
You look/seem as if/as thought you had been there before.
Maybe/Perhaps/ she is ill.
He is probably ill.
He is likely ill.
It is possible that he is late
4) 注释判断
He can remember so many English words, that is (to say) he is a living dictionary.(活字典)
5) 正反判断
That sounds all right, but in fact it is not.
6) 比较判断
It is more a picture than a poem.
7) 互斥判断
He or you are wrong.
Either he is right or I am.
英语中句子类型有哪四种
楼主说的这个范围太广了~
不过要快速的判断句子句式,个人见解
如何判断倒装句、强调句、祈使句或者说从句的类型,
1.首先你要熟知这些句子的性质与特点(这个是要下功夫学习,在校期间通过老师讲解再积累)
2.经验问题(英语老师能够快速的判断句式并理解,是因为多年来的见到数多句式,熟练了,自然而然,能够轻易判断)
从第一步做起吧,若有基础了,就开始训练(包括做题、看英语文章……)
太郁闷了,刚帮楼主找了句式,好像没有提交到(你可以直接在网上输句式名可以查到)
直接说你的第二个问题吧~
高中常见的句式一般是:宾语从句、定语从句和状语从句这几种居多.
判断方法可以粗略的说为,首先找到复合句的从句部分,在分析从句是做整个句子的宾语部分(宾语从句),做定语及定语从句.(方法越简单越易理解)
举个例:He is the man whom/ that I saw yesterday.他就是我昨天见的那个人.
从汉译来看简单些,I saw yesterday作man的定语,所以判断是定语从句,其中whom/that在从句中作宾语)
这个方法简单可以大致判断从句的类型,如果具体到定语从句本身的判断,就得靠楼主平时多多努力,积累了)
英语句子成分应当如何判断?高中常见句式结构及其用法
按句子的用途分为四种:陈述句、疑问句、祈使句、感叹句。
1、陈述句(Declarative Sentence)是陈述一个事实或者说话人的看法的句型。陈述句又分为肯定的陈述句和否定的陈述句,简称为肯定句(The Affirmative Sentence)和否定句(The Negative Sentence)。
2、疑问句是按照句子的语气分出来的一个类,它与陈述句、感叹句、祈使句的最大区别就是它的疑问语气;是问一些事情的,表达的内容并不是陈述,所以是不确定的;主要有四大句型,一般疑问句、选择疑问句、特殊疑问句和反意疑问句。
3、祈使句(Imperative Sentence)是英语中的一个句式,也是用于表达命令、请求、劝告、警告、禁止等的句子。祈使句最常用于表达命令,因此在学校文法中也常称为命令句。
4、感叹句有多种表现形式,有时一个单词、短语或一个词组也可成为感叹句。有时陈述句、疑问句以及祈使句也可以转化成感叹句。
扩展资料
陈述句的五种基本句型:
(1)?主语+连系动词+表语
(2) 主语+谓语(不及物动词)
(3) 主语+谓语(及物动词)+宾语
(4) 主语+谓语(及物动词)+间接宾语+直接宾语
(5) 主语+谓语(及物动词)v.+宾语+宾语补足语
感叹句主要的表现形式只有两种,即what和how引导的感叹句。what修饰名词(名词前可加冠词和形容词),how修饰形容词、副词或动词。
参考资料:
英语句子的类型有哪些?
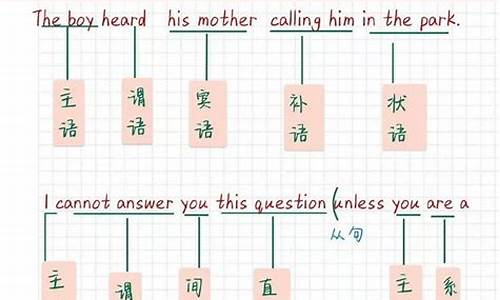
句子成分:英语句子成分分为七种:主语、谓语、宾语、定语、状语、表语、宾语补足语。1、主语是句子所要说的人或事物,回答是“谁”或者“什么”。通常用名词或代词担任。如:I’m Miss Green.(我是格林**)2、谓语动词说明主语的动作或状态,回答“做(什么)”。主要由动词担任。如:Jack cleans the room every day. (杰克每天打扫房间)3、表语在系动词之后,说明主语的身份或特征,回答是“什么”或者“怎么样”。通常由名词、代词或形容词担任。如:My name is Ping ping .(我的名字叫萍萍) 4、宾语表示及物动词的对象或结果,回答做的是“什么”。通常由名词或代词担任。如:He can spell the word.(他能拼这个词)有些及物动词带有两个宾语,一个指物,一个指人。指物的叫直接宾语,指人的叫间接宾语。间接宾语一般放在直接宾语的前面。如:He wrote me a letter . (他给我写了一封信)有时可把介词to或for加在间接宾语前构成短语,放在直接宾语后面,来强调间接宾语。如:He wrote a letter to me . (他给我写了一封信)5、定语修饰名词或代词,通常由形容词、代词、数词等担任。如:Shanghai is a big city .(上海是个大城市)6、状语用来修饰动词、形容词、副词,通常由副词担任。如:He works hard .(他工作努力)7、宾语补足语用来说明宾语怎么样或干什么,通常由形容词或动词充当。如:They usually keep their classroom clean.(他们通常让教室保持清洁) / He often helps me do my lessons.(他常常帮我做功课) / The teacher wanted me to learn French all by myself.(老师要我自学法语)☆同位语通常紧跟在名词、代词后面,进一步说明它的情况。如:Where is your classmate Tom ?(你的同学汤姆在哪里?)
英语句子的种类和用法,有哪些啊?
英语中句子类型有哪四种
英语句子种类有两种分类:
1.按句子的用途分为四种:
陈述句、疑问句、祈使句、感叹句2.按句子结构可分为:
简单句、并列句、复合句
英语中句子种类有哪些?
宾语从句 主语从句 表语从句 双宾语从句 状语从句
英语的句子类型有哪几种
his head from a round window of the barn.
`Whet are ye for?' he shouted. `T' maister's
英语句子有那些种类
主谓宾
主系表
这是句子的构成
主语,谓语动词,宾语
名词代词是主语,谓语是动词,宾语和主语的构成一致
但是宾语要用宾格
英语里面有几种句子类型组成句子的结构有什么,比如什
1简单句、并列句、复合句
根据语法形式,即句子的结构,英语的句子可分为简单句、并列句和复合句.
1简单句
句型:主语+谓语
只包含一个主谓结构,而句子的各个结构都只由单词或短语表示.简单句有五种基本句型,详见第十七章.
They are playing baseball in the garden.
他们正在公园里打棒球.
Her brother and sister both are teachers.
她的哥哥和姐姐都是老师.
2并列句
句型:简单句+并列连词+简单句
(常见的并列连词有and,but,or)
并列句是由两个或两个以上的简单句连接而成.并列句中的各简单句意义同等重要,相互之间没有从属关系,是平行并列的关系.它们之间用连词连结.
My friend was at home,and we talked for along time.
我的朋友在家,我们谈了好长时间.
英语初中相关语法知识 句子成分主要是怎么判断的 都有哪些固定短语 特殊疑问句一般疑问句如何区分
一、陈述句:是用来陈述一件事情或表示一种看法,可分为肯定句和否定句两种形式。
1、谓语动词是be动词,助动词he, has, will,情态动词can等时,只要直接在这些词后面加not就构成否定形式。
eg. Lily has already read this new book. (改为否定句)
Lily ______ ______ this new book ________.
2、谓语动词是行为动词而又没有助动词或情态动词时,必须在谓语动词前加助动词,一般现在时加助动词do ,第三人称单数加does,一般过去时加did,再和not构成否定结构。必须指出的是:don't, doesn't, didn't后都用动词原形。
eg.1)Jill has lunch at school every day. (改为否定句)
Jill _____ _____ lunch at school every day.
2)The children had a good time at the party. (改为否定句)
The children ______ _____ a good time at the party.
3)Rose didn't drink any milk this morning.(改为肯定句)
Rose ______ ______ milk this morning.
二、疑问句:是用来提出问题的句子。
A.一般疑问句:以be动词, he /has/do等助动词、can/may等情态动词开头,以yes或no来回答的问句。
它的基本结构是:Be/He /Has/Did等助动词(包括情态动词)+主语+谓语(包括表语)+┄?回答常用简略回答。
1、谓语动词是be动词、助动词、情态动词时,只要直接把这些词置于句首,句末改成问号。
eg. There's something wrong with his bike.(改成疑问句)
______ _____ _______ wrong with his bike?
2、谓语动词是行为动词时,必须在句首加上助动词Do、Does(三单)、Did(过去式)加上这些助动词后,句子中谓语动词必须用原形。
eg. 1)Edison built a science lab himself when he was ten. (改成疑问句)
______ Edison ______ a science lab himself when he was ten?
2)Those Japanese like Chinese food.(改成疑问句)
______ those Japanese ________ Chinese food?
注意:在把肯定句改成否定句或一般疑问句的时候,要注意句中是否有already、some、something、somebody等词,如果有也必须进行改变,already要改成yet,some、something、somebody等分别改成any、anything、anybody等。另外,在改成否定句的时候注意把too改成either,both改成neither,all改成none等.在改成一般疑问句的时候,常常把第一人称I、we改成第二人称you。
B.特殊疑问句:以疑问代词或疑问副词开头,提出疑问的句子。
它的基本结构是:特殊疑问词+一般疑问句语序。但是如果疑问词在句子中作主语或作主语的定语,就用特殊疑问词+陈述句语序。常用的疑问词有:what, who(whom), whose,which,when,where,how,why等,回答时针对问句中的代词和副词来回答,不用yes或no来回答。
1)对指物名词或谓语动词提出疑问,疑问词用what
①The twins were making a kite when their mother came in. (划线提问)
______ _____ the twins _____ when their mother came in?
②Mrs Turner asked her son to buy some eggs for supper. (划线提问)
_______ ______ Mrs Turner ask her son ______ _______?
2)对名词前定语提出疑问,疑问词应用which,而且必须和名词连用。
I'm going to take the shirt on the right.(划线提问)
______ _____ are you going to take?
3)对指人名词或代词提问用who,作宾语时提问用whom。
eg.Li Ping,they,his father
4)对物主代词和名词所有格提问用whose。
eg. Li Ping's coat→Whose coat my father→Whose father
5)对具体时间提出疑问,如 in the morning,last Sunday等,疑问词用when;对具体几点钟提问,疑问词应用what time。
6)对具体地点提出疑问,疑问词应用where。
The pupils are hing a picnic at the foot of the hill. (划线提问)
_____ _____ the pupils hing a picnic?
7)对表原因的从句提问,常见的有because引导的从句,疑问词应用why。
Xiao Cheng didn't go to the farm with us because he was ill. (划线提问)
_______ _____ Xiao Cheng go to the farm with us?
8)对方式或程度等提出疑问,用疑问词How。
eg. go by bike like very much
9)对数量提出疑问,疑问词为How many,要注意how many必须跟名词的复数形式。
eg. two hundred sheep→How many sheep
10)对价格提出疑问,疑问词用How much。
eg. I paid fifty yuan for the sweater.
______ ______ did you pay for the sweater?
11)对时间长度提出疑问,疑问词应用How long。
eg. I've worked in that factory for two years. (划线提问)96中考题
______ _____ _______ you worked in that factory?
12)对时间频率,如 once a year, twice a week等提问,疑问词用How often。
13)对具体次数,如 once, twice, three times等提问,疑问词用How many times。
eg. ______ did he call you the day before yesterday?Twice. 96中考题
A.What time B.How many times C.How much D.How long
14)对in+一段时间提问,疑问词一般用How soon。
eg. Jane and her brother will finish the work in two hours. (划线提问)
_____ _____ _____ Jane and her brother finish the work?
15)对距离提出疑问,疑问词用How far。
eg. It's about two kilometres from here to the country.(划线提问)
______ _____ _____ _____ from here to the country?
16)另外,对日期、星期、天气等提出疑问,则分别用
What's the date?
What day is it ? 如果是过去时间,就用was代替is。
What's the weather like?
练习题
1)She does exercises at home in the evening.(改成否定句、一般疑问句)
She ______ ______ exercises at home in the evening.
______ she _____ exercises at home in the evening?
2)He said something important at the meeting.(改为否定句,一般疑问句)
He _____ ______ ______ important at the meeting.
______ he ______ ______ important at the meeting?
3)It'll take them three weeks to finish the work.(划线提问)
______ ______ _______ it take them to finish the work?
4)I he to wash all the plates and things after meals.(划线提问)
_____ _____ you he to wash all the plates and things?
5)The woman in the red coat is her mother.(划线提问)
______ ______ is her mother?
6)Li Ping spent twenty yuan on the dictionary.(划线提问)
_____ ____ ____ Li Ping _____ on the dictionary?
思考题
1)The worker's visited the factory already.(改成否定句、一般疑问句)
The worker _____ _____ the factory ______.
____ the worker ___ the factory __?
2)Both of his parents are workers.(改成否定句)
___ of his parents ______ a worker.
3)He went to the park with his sister.(划线提问)
_____ ____ ____ he go to the park?
4)We really enjoyed working on the farm.(划线提问)
What _____ you really enjoy ______?
5)She writes to her parents once a week.(划线提问)
_______ ______ ______ she write to her parents?
6)Our P.E teacher has been at this school since he came.(划线提问)
______ ______ ______ our P.E teacher been at this school?
一、陈述句:是用来陈述一件事情或表示一种看法,可分为肯定句和否定句两种形式。
1、谓语动词是be动词,助动词he, has, will,情态动词can等时,只要直接在这些词后面加not就构成否定形式。
eg. Lily has already read this new book. (改为否定句)
Lily ______ ______ this new book ________.
2、谓语动词是行为动词而又没有助动词或情态动词时,必须在谓语动词前加助动词,一般现在时加助动词do ,第三人称单数加does,一般过去时加did,再和not构成否定结构。必须指出的是:don't, doesn't, didn't后都用动词原形。
eg.1)Jill has lunch at school every day. (改为否定句)
Jill _____ _____ lunch at school every day.
2)The children had a good time at the party. (改为否定句)
The children ______ _____ a good time at the party.
3)Rose didn't drink any milk this morning.(改为肯定句)
Rose ______ ______ milk this morning.
二、疑问句:是用来提出问题的句子。
A.一般疑问句:以be动词, he /has/do等助动词、can/may等情态动词开头,以yes或no来回答的问句。
它的基本结构是:Be/He /Has/Did等助动词(包括情态动词)+主语+谓语(包括表语)+┄?回答常用简略回答。
1、谓语动词是be动词、助动词、情态动词时,只要直接把这些词置于句首,句末改成问号。
eg. There's something wrong with his bike.(改成疑问句)
______ _____ _______ wrong with his bike?
2、谓语动词是行为动词时,必须在句首加上助动词Do、Does(三单)、Did(过去式)加上这些助动词后,句子中谓语动词必须用原形。
eg. 1)Edison built a science lab himself when he was ten. (改成疑问句)
______ Edison ______ a science lab himself when he was ten?
2)Those Japanese like Chinese food.(改成疑问句)
______ those Japanese ________ Chinese food?
注意:在把肯定句改成否定句或一般疑问句的时候,要注意句中是否有already、some、something、somebody等词,如果有也必须进行改变,already要改成yet,some、something、somebody等分别改成any、anything、anybody等。另外,在改成否定句的时候注意把too改成either,both改成neither,all改成none等.在改成一般疑问句的时候,常常把第一人称I、we改成第二人称you。
B.特殊疑问句:以疑问代词或疑问副词开头,提出疑问的句子。
它的基本结构是:特殊疑问词+一般疑问句语序。但是如果疑问词在句子中作主语或作主语的定语,就用特殊疑问词+陈述句语序。常用的疑问词有:what, who(whom), whose,which,when,where,how,why等,回答时针对问句中的代词和副词来回答,不用yes或no来回答。
1)对指物名词或谓语动词提出疑问,疑问词用what
①The twins were making a kite when their mother came in. (划线提问)
______ _____ the twins _____ when their mother came in?
②Mrs Turner asked her son to buy some eggs for supper. (划线提问)
_______ ______ Mrs Turner ask her son ______ _______?
2)对名词前定语提出疑问,疑问词应用which,而且必须和名词连用。
I'm going to take the shirt on the right.(划线提问)
______ _____ are you going to take?
3)对指人名词或代词提问用who,作宾语时提问用whom。
eg.Li Ping,they,his father
4)对物主代词和名词所有格提问用whose。
eg. Li Ping's coat→Whose coat my father→Whose father
5)对具体时间提出疑问,如 in the morning,last Sunday等,疑问词用when;对具体几点钟提问,疑问词应用what time。
6)对具体地点提出疑问,疑问词应用where。
The pupils are hing a picnic at the foot of the hill. (划线提问)
_____ _____ the pupils hing a picnic?
7)对表原因的从句提问,常见的有because引导的从句,疑问词应用why。
Xiao Cheng didn't go to the farm with us because he was ill. (划线提问)
_______ _____ Xiao Cheng go to the farm with us?
8)对方式或程度等提出疑问,用疑问词How。
eg. go by bike like very much
9)对数量提出疑问,疑问词为How many,要注意how many必须跟名词的复数形式。
eg. two hundred sheep→How many sheep
10)对价格提出疑问,疑问词用How much。
eg. I paid fifty yuan for the sweater.
______ ______ did you pay for the sweater?
11)对时间长度提出疑问,疑问词应用How long。
eg. I've worked in that factory for two years. (划线提问)96中考题
______ _____ _______ you worked in that factory?
12)对时间频率,如 once a year, twice a week等提问,疑问词用How often。
13)对具体次数,如 once, twice, three times等提问,疑问词用How many times。
eg. ______ did he call you the day before yesterday?Twice. 96中考题
A.What time B.How many times C.How much D.How long
14)对in+一段时间提问,疑问词一般用How soon。
eg. Jane and her brother will finish the work in two hours. (划线提问)
_____ _____ _____ Jane and her brother finish the work?
15)对距离提出疑问,疑问词用How far。
eg. It's about two kilometres from here to the country.(划线提问)
______ _____ _____ _____ from here to the country?
16)另外,对日期、星期、天气等提出疑问,则分别用
What's the date?
What day is it ? 如果是过去时间,就用was代替is。
What's the weather like?
练习题
1)She does exercises at home in the evening.(改成否定句、一般疑问句)
She ______ ______ exercises at home in the evening.
______ she _____ exercises at home in the evening?
2)He said something important at the meeting.(改为否定句,一般疑问句)
He _____ ______ ______ important at the meeting.
______ he ______ ______ important at the meeting?
3)It'll take them three weeks to finish the work.(划线提问)
______ ______ _______ it take them to finish the work?
4)I he to wash all the plates and things after meals.(划线提问)
_____ _____ you he to wash all the plates and things?
5)The woman in the red coat is her mother.(划线提问)
______ ______ is her mother?
6)Li Ping spent twenty yuan on the dictionary.(划线提问)
_____ ____ ____ Li Ping _____ on the dictionary?
思考题
1)The worker's visited the factory already.(改成否定句、一般疑问句)
The worker _____ _____ the factory ______.
____ the worker ___ the factory __?
2)Both of his parents are workers.(改成否定句)
___ of his parents ______ a worker.
3)He went to the park with his sister.(划线提问)
_____ ____ ____ he go to the park?
4)We really enjoyed working on the farm.(划线提问)
What _____ you really enjoy ______?
5)She writes to her parents once a week.(划线提问)
_______ ______ ______ she write to her parents?
6)Our P.E teacher has been at this school since he came.(划线提问)
______ ______ ______ our P.E teacher been at this school?
句型转换题是中考常见题型,它主要用来考查大家对句子结构的构成、变化的掌握及在行文中的运用等,类型繁多。现以近两年中考题为例,分类介绍如下:
[第一类] 改成否定句
英语中有关否定的结构各不相同,除动词部分构成的否定外,还有名词、代词的否定、部分否定、否定转移、以及一些表示否定意义的短语或句型等。
一、含有连系动词、情态动词等助动词的句子改为否定句时,在连系动词、情态动词等的后面加not就行了。如:(划线部分为正确答案,下同。)
1. He was late for school yesterday. (2005黑龙江省泰州市)
He wasn’t late for school yesterday.
2. The students of No.2 Middle School he gone for a picnic already. (2004新疆)
The students of No.2 Middle School hen’t gone for a picnic yet.
二、祈使句变否定句一般在其前加don’t。如:
3. Open the window. (2005江苏省)
Don’t open the window.
三、实义动词的否定式是在实义动词前加don’t, doesn’t, didn’t等。如:
4. She does the housework every day. (2005黑龙江省哈尔滨市)
She doesn’t do the housework every day.
5. He returned the book to the library this morning. (2004重庆市)
He didn’t return the book to the library this morning.
注意:变否定句时须注意某些词语的变化,如some改为any, something改为anything, already改为yet, both改为neither, all改为none等。又如:
6. Both of them are my best friends. (2004甘肃省兰州市)
Neither of them is my best friend.
[第二类] 改为疑问句
可分为一般疑问句、选择疑问句和反意疑问句。
一、变一般疑问句时,含有连系动词、情态动词的句子,只需将它们移至句首,第一个字母变为大写,句尾改为问号即可。含有实义动词的句子,在实义动词前加do, does, did等。变化过程中也要注意某些词语和人称的变化。如:
7. There’s something to eat in the cupboard.(2005贵州省贵阳市)
Is there anything to eat in the cupboard?
8. Kate does morning exercises every day. (2004山东省济南市)
Does Kate do morning exercises every day?
9. Ann returned the book to the library yesterday. (2005四川省成都市)
Did Ann return the book to the library yesterday?
二、变选择疑问句时,如果该句是一般疑问句,则在后面直接加“or+另一选择部分”就行了;若是陈述句,则要先变成一般疑问句。如:
10. John is an American. (用a Canadian改为选择疑问句)(2004新疆)
Is John an American or a Canadian?
三、变反意疑问句时,要注意“前肯后否”和“前否后肯”,还要注意一些特殊形式的反意疑问句。如:
11. She has hardly had anything this morning, has she?(2005山东省泰安市)
12. You will meet your friends at the railway station, won’t you?(2004重庆)
13. She had nothing for breakfast, did she?(2005青海)
14. There was no time for the twins to go shopping, was there?(2004黑龙江省哈尔滨市)
1. 词类名词----------表示人或事物的名称形容词-------表示人或事物的特征副词----------修饰动词、形容词、或其他副词动词----------表示动作或状态代词----------代替名词、数词数词----------表示数量或顺序冠词----------限制名词的意义介词-------表示名词、代词和其他词的关系连词-------连接词与词或句与句感叹词-----表示说话时的感情或语气 一.主语:主语(subject) 是一个句子的主题( theme), 是句子所述说的主体。它的位置一般在一句之首。可用作主语的有单词、短语、从句乃至句子。
1.名词作主语。 如:A tree has fallen across the road. (一棵树倒下横在路上。)
Little streams feed big rivers. ( 小河流入大江。)
2.代词用作主语。如:You’re not far wrong. (你差不多对了)。
He told a joke but it fell flat. (他说了个笑话,但没有引人发笑
3.数词用作主语。如:Three is enough. 三个就够了。
Four from seven lees three. 7减4余3。
4.名词化的形容词用作主语。
The idle are forced to work. 懒汉被迫劳动。
Old and young marched side by side. 老少并肩而行。
5.副词用作主语。如:Now is the time. 现在是时候了。
Carefully does it. 小心就行。
6.名词化的介词作主语。如:The ups and downs of life must be taken as they come.
我们必须承受人生之沉浮。
7.不定式用作主语。 如:To find your way can be a problem.你能否找到路可能是一个问题。
It would be nice to see him again.
如能见到他,那将是一件愉快的事。
8. 动名词用作主语。如:Smoking is bad for you. 吸烟对你有害。
Watching a film is pleasure, making one is hard work.
看**是乐事, 制作影片则是苦事。
9. 名词化的过去分词用作主语。如:The disabled are to receive more money.
残疾人将得到更多的救济金。
The deceased died of old age.
死者死于年老。
10. 介词短语用作主语。如:To Beijingis not very far. 到北京不很远。From Yenan to Nanniwan was a three-hour ride on horseback.
从延安到南泥湾要三个小时。
11.从句用作主语。如: Whenever you are ready will be fine.
你无论什么时候准备好都行。
Because Sally wants to lee doesn’t mean that we he to.
不能说萨利要走因而我们也得走。
12.句子用作主语。如:”How do you do ?” is a greeting.“你好”是一句问候语。
二.谓语
谓语(predicate) 或谓语动词(predicate verb) 的位置一般在主语之后。谓语由简单动词或动词短语(助动词或情态动词+主要动词)构成。
1.由简单的动词构成。
(1). What hened? 发生了什么事?
(2). He worked hard all day today. 他今天苦干了一天。
(3). The plane took off at ten o’clock. 飞机是十点起飞的。
2.由动词短语构成的谓语。
(1). I am reading. 我在看书。
(2). What’s been keeping you all this time? 这半天你在干什么来着?
(3). You can do it if you try hard. 你努力就可以做到。
3.英语常用某些动作名词代替表动态的谓语动词,表生动。这种动作名词之前常用没有多大意义的动词he, get, take, give 等。如:
(1). I had a swim yesterday. 我昨天游了一次水(had a swim 代替了swam)
(2). Take a look at that! 你看看那个!(take a look 代替了 look)
(3). He ge a sigh. 他叹了口气。(ge a sigh 代替了sighed)
(4). I got a good shake-up.我受到了很大的震动。(a good shake-up 代替了was shaken up thoroughly(充分,彻底的))
三.表语
表语的功能是表述主语的特征、状态、身份等。它也可以说是一种主语补语。它位于联系动词之后,与之构成所谓的系表结构。在系表结构钟,联系动词只是形式上的谓语,二真正起谓语作用的则是表语。可以作表语的词有:名词、代词、数词、形容词、副词、不定式、动名词、分词、介词短语、从句等。
1.The wedding was that Sunday. 婚礼是在那个星期天举行的。(名词)
2.So that’s that. 就是这样。(代词)
3.We are seven. 我们一共7人。(数词)
4.Are you busy? 你有空吗?(形容词)
5.Are you there? 你在听吗?(电话用语)(副词)
Is anybody in? 里面有人吗? (副词)
6.All I could do was to wait. 我只能等待。(不定式)
My answer to his threat(威胁) was to hit him on the nose.
我对他的威胁的回答是照他的鼻子打去。(不定式)
7.Complimenting(赞美,祝贺) is lying. 恭维就是说谎。(动名词)
Is that asking so much? 这是要的高了吗?(动名词)
8.I was so much surprised at it. 我对此事感到很惊讶。(过分)
I’m very pleased with what he has done. 我对他所做的很满意。(过分)
9.She is in good health. 她很健康。(介词短语)
The show is from seven till ten. 演出时间为7点至10点。(介词短语)
10.Is that why you were angry? 这就是你发怒的原因吗?(从句)
11.This is where I first met her. 这就是我初次与她会面的地方。(从句)
补充:
能做系动词的实义动词:
come , go , run, turn ,get , become , keep , stay , make (表变化的动词)
fell,sound ,smell , look , taste (感观动词)
seem, ear (似乎,好像)
例如:
1.Our dream has come true. 我的梦想实现了。(Come后常加 easy ,loose natural 等)
2. He fell sick. 他病了。
Keep fit.保重。
Keep作为系动词还常接quiet ,calm ,cool, well, warm ,silent,clean,dry
3.The well ran dry. 这口井干枯了。(short , loose , wild , cold 等)
4.A thin person always seems to be taller than he really is.
一个瘦个子似乎比他的实际高度要高些。
四.宾语
宾语(object)在句中主要充当动作的承受者,因此一般皆置于及物动词之后。如:
Our team beat all the others. 我们的球队打败了所有其他球队。
可以用作宾语的有:名词、代词、数词、名词化的形容词、副词、不定式、动名词、名词化的分词、从句等。
1.Do you fancy a drink? 你想喝一杯吗?(名词)
2.They won’t hurt us. 他们不会伤害我们。(代词)
3.If you add 5 to 5, you get 10. 5加5等于10。(数词)。
4.I shall do my possible. 我将尽力而为。(名词化形容词)
5.He left there last week. 他上个星期离开了那里。(副词)
6.Does she really mean to lee home? 她真的要离开家吗?(不定式)
7.He never did the unexpected(想不到的,意外的).
他从不做使人感到意外的事。(名词化的分词)
8.Do you understand what I mean? 你明白我的意思吗?(从句)
扩展:
宾语中有些动词需要两个同等的宾语,即直接宾语(direct object)与间接宾语(indirect object)。直接宾语一般指动作的承受者,间接宾语指动作所向的或所为的人和物(多指人),具有这种双宾语的及物动词叫做与格动词(dative verb), 常用的有:answer, bring, buy, do, find, get, give, hand, keep, lee, lend, make, offer, owe, pass, pay, play, promise, read, se, sell, send, show, sing, take 等,间接宾语一般须与直接宾语连用,通常放在直接宾语之前。如:I he found him a place. 我给他找到了一个职位。
五.补语
补语(complement)是一种补足主语和宾语的意义的句子成分。补足主语意义的句子成分叫做主语补语(subject complement),补足宾语意义的句子成分叫做宾语补语(object complement).
(1). 容词用作主语补语是常置于主语之前,后有逗号。
Tired and sleepy, I went to bed. 我又累又困,就去睡了。
有时可以置于主语之后,前后都有逗号,与非限定性定语相似。如:
The man, cruel beyond belief, didn’t listen to their pleadings.
那人不可置疑地残酷,不听取他们的恳求。
(2).可以用做宾语补语的有名词、形容词、不定式、动名词、分词、介词短语等
1.They named the child Jimmy. 他们将孩子命名为吉米。(名词用作并与补语)
2.My mother looks so young that you would think her my sister.
我的母亲面很嫩,你会以为她是我的姐姐(名词短语作宾语补语)
3. He boiled the egg hard. 她将鸡蛋煮老了。(形容词用作宾语补语)
3.I found the book very interesting.我发现那本书很有趣。(形容词短语用作宾补)
4.The comrades wanted Dr. Bethune to take cover.
同志们要白求恩大夫隐蔽一下。(不定式用作宾语补语)
5.I call this rog Peter to pay Paul.我把这个叫做拆东墙补西墙。(动名作宾补
6.Don’t take his kindness for granted.不要把他的友善看作是当然的事。
六.定语
定语是用来说明名词(代词)的品质与特征的词或一组词。可用作定语的有:形容词、名词、代词、数词、副词、不定式、动名词、分词、介词短语、从句和句子等。
1.形容词用作定语是大量的。
(1). She is a natural musician. 她是一位天生的音乐家。
(2). He must be the best violinist alive.他一定是最好的在世的小提琴手了。(后置定语)
2. 名词用作定语。如
(1). A baby girl 女婴
(2). well water 井水
(3). Sports car 双座轻型汽车
(4). A fool’s paradise 梦幻的天堂
2.代词作定语。
(1). Your hair needs cutting. 你该理发了。(物主代词用作定语)
(2). Everybody’s business is nobody’s business. 负责就是无人负责。
(不定代词所有格作定语)
3.数词作定语
(1). There’s only one way to do it. 做此事只有一法。
(2). Do it now, you may not get a second chance.
现在就干吧,你可能再没有机会了。
基数词用作后置定语: page 24 Room 201 the year 1949
4. 副词充当定语时常后置,如:
the room above 楼上的房间 the world today 今日世界
the way out 出路 a day off 休息日
5.不定式用作定语
(1). Her promise to write was forgotten.她忘记了答应写信的事。
(2). That’s the way to do it.那正是做此事的方法。
6.动名词用作定语.
A walking stick 拐杖 sleeping pills 安眠药
eating implements 吃饭用具 learning method 学习方法
7.分词充当定语
a sleeping child 正在睡中的小孩 a drinking man 嗜酒者
a retired worker 一个退休工人 a faded flower 一朵谢了的花
7.介词短语用作定语。
(1). This is a map ofChina. 这是一幅中国地图。
(2). The wild look in his eyes spoke plainer than words.
他那凶暴的目光说明得再清楚不过了。
8.从句用作定语,即定语从句
The car that’s parked outside is mine. 停在外面的车是我的。
Your car, which I noticed outside, has been hit by another one.
我在外面看见你的汽车了,它给另一辆车撞了。
七.同谓语
当两个指同一事物的句子成分放在同等位置时,一个句子成分可被用来说明或解释另一个句子成分,前者就叫做后者的同谓语(ositive).这两个句子成分多由名词(代词)担任,同谓语通常皆放在其说明的名词(代词)之后。
1.名词用作同谓语是大量的。
(1). We he two children, a boy and a girl.我们有两个孩子,一男一女。
(2)We, the Chinese people, are determined to build China into a powerful and prosperous country. 我们中国人民决心将中国建成一个强大的繁荣的国家。
2.代词用作同谓语。
(1)。They all wanted to see him. 他们都想见他。
(2)。Let’s you and me go to work, Oliver. 咱们俩去工作吧。
3.数词用作同谓语。
(1)。Are you two ready?你们俩准备好了吗?
(2)。They two went, we three stayed behind.他们俩去了,我们三个留了下来。
4.不定式与动名词用作同谓语。
(1)。Their latest proposal, to concentrate on primary education, has met with some opposition.他们最近提出了集中全力于初等教育的提议遭到了某些人的反对。
(2)。The first plan, attacking at night, was turned down.
第一个是夜袭,被拒绝了。
5.Of 短语用作同谓语
The city of Rome 罗马城 the art of writing 写作艺术
The vice of smoking 吸烟嗜好
6.从句用同谓语,即同谓语重句
(1)。The news that we are hing a holiday tomorrow is not true.
明天放的消息不确。
(2)。We are not investigating the question whether he is trustworthy.
我们不是在调查他是否可信赖的问题。
八.状语
状语(adverbial)是修饰动词、形容词、副词以及全句的句子成分。。如:
1.The girl is improving remarkably. 这个女孩大有进步。
2.可用作状语的有副词、名词、代词、数词、形容词、不定式、分词、介词短语、从句等。
(1)。副词最常用作状语,位置比较灵活,可置句末、句首和句中。
He speaks the language badly but read it well.
这种语言,他讲得不好,但阅读能力很强。
Naturally we expect hotel guests to lock their doors.
当我们期望旅馆的旅客把房门锁上。
3.状语按用途来分,可以分为时间、地点、方式、原因、结果、目的、条件、让步、程度、方式、伴随等
(1)。时间状语,多位于句末和句首,有时亦可置于句中
Shall we do the shopping today or tomorrow?
InChinanow leads the world.
(2).地点状语,多置于句末,有时也位于句首和句中。
There are plenty of fish in the sea.
She kissed her mother on the platform(月台).
(3)。原因状语,包括表理由的状语,多置于句末,有时亦可置于句首。
Because he was ill ,Tom lost his job.
I eat potatoes because I like them.
(4). 结果状语,多由不定式、分词和从句表示,常位于句末。
She woke(醒) suddenly to find someone standing in the doorway.
She spoke so softly that I couldn’t hear what she said.
(5). 目的状语,多由不定式、介词短语和从句等表示,常位于句末,强调时可以置于句首。
He ran for shelter(隐蔽处).他跑去避雨。
In order to get into a good school, I must study even harder.
(6). 条件状语。多由短语和从句表示,常置于句末和句首。
We’ll be lucky to get there before dark.
If he were to come, what should we say to him?
(7). 让步状语,由短语和从句表示,常置于句末和句首。
For all his money, he didn’t seem hy. 他尽管有钱,但似乎并不幸福。
He helped me although he didn’t know me.
(8).程度状语。常由副词、介词短语及从句等表示。
The lecture is very interesting.
To what extent would you trust them? 你对他们信任程度如何?
(9)。伴随状语,常由短语和独立主格等表示。对位于句末和句首。
My train starts at six, arriving atChicagoat ten.
He stood there ,pipe(烟斗) in mouth.









