您现在的位置是: 首页 > 经典语录 经典语录
_初中英语句子成分练习题
tamoadmin 2024-08-16 人已围观
简介1.解析初中英语句子成分2.求一个英语句子成分分析3.初中英语句子成分分析4.词类和句子成分的关系初中英语知识点梳理5.初中英语句子成分分析法6.请大家告诉我初中英语的特殊句式(宾语从句)啊这一类的。7.关于英语句子成分的问题!!!8.初中英语句子成分划分(she主语)( heard谓语)( a girl 宾语)(sing a song宾补)( yesterday时间状语)hear/ see/fi
1.解析初中英语句子成分
2.求一个英语句子成分分析
3.初中英语句子成分分析
4.词类和句子成分的关系初中英语知识点梳理
5.初中英语句子成分分析法
6.请大家告诉我初中英语的特殊句式(宾语从句)啊这一类的。
7.关于英语句子成分的问题!!!
8.初中英语句子成分划分
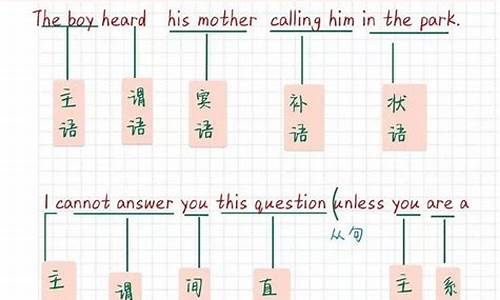
(she主语)( heard谓语)( a girl 宾语)(sing a song宾补)( yesterday时间状语)
hear/ see/find/watch/listen to/ notice sb+doing/ do sth
hear/see/find/feel等+ sb+do sth (用动词原形表示全部过程,或动作持续时间很短),而用动词ing 表示一部分过程,或动作正在进行。
如:I heard her crying when I passed her room.(heard her crying 表示那是正在哭,听到了哭的一部分,不是全部)
I saw him pick an le.( 苹果持续时间很短)
I listened to him read a text.( 表示从头到尾听到他读完一篇课文)
解析初中英语句子成分
一、五种简单句基本句型
1.“主语 + 谓语”(即“主谓”句型)
这一句型英汉语言结构形式完全相同,说明“某人或某物如何动作”,或者说“某人或某物自身怎样运动”。
例:They arrived in Harbin yesterday morning.
分析:“they”(主语)“arrived”(谓语)。
2.“主语 + 谓语 + 宾语”(即“主谓宾”句型)
这一句型英汉语言的结构形式完全相同,用以说明“某人或某物做什么事情”,或者说“某人或某物发出了动作,并且其动作涉及到另一个人或物”。
例:I study English.
分析:“I”(主语)“study”(谓语动作)“English”(宾语即动作涉及的对象)。
3.“主语 + 谓语 + 间接宾语 + 直接宾语”(即“主谓双宾”句型)
这一句型英汉语序结构相同,说明“某人为谁(间接宾语为人)做某事”,或者说“某人或物的运动涉及到两个对象,其中一个间接对象为人,另一个为物”。
例:Our teacher taught us English.
分析:“our teacher”(主语)“教”(谓语动作)“us”(间接宾语)“English”(直接宾语)。
4.“主语 + 谓语 + 宾语 + 宾语补足语”(即“主谓宾宾补”句型)
这一句型说明“某人或某物要求(使、让)某人做什么”或“某人感觉某人或物怎么样”。
例: He asked her to go there.
分析:“he”(主语)“asked”(谓语动作)“her”(宾语即动作涉及的对象)“to go there”(补语--补充说明宾语做什么)。
5.“主语 + 系动词+ 表语”(即“主系表”句型)
这一句型用以说明“某人(某物、某事、某种概念)具有什么特征或处于什么状态”。汉语的“是”字结构属于这一英语句型的形式之一。常用的系动词有be, keep,lie, remain, stand, become, fall, get, go, grow, turn, look, feel, seem, smell, sound, taste, 等。
例: I am a teacher. 我是一名老师
分析:“I”(主语)“am”(系动词)“a teacher”(表语—即表明主语的身份)。
二、句子成分名词解释
1.主语:句子所陈述的对象。
2.谓语:主语发出的动作。一般是有动作意义的动词。
3. 宾语:分为动词宾语和介词宾语,属于动作的承受者。
4. 系动词:表示状态或状态变化的动词,没有实际的动作意义。如 be, 感官系动词(look, sound, smell, taste 和 feel)、保持类系动词(keep, stay 和 remain)、状态变化类系动词(become、get、turn 和 go)等。
5. 表语:紧跟系动词后面的成分。
6. 定语:修饰名词或代词的成分。
7. 状语: 修饰形容词、副词、动词或句子的成分。
8. 补语:分为宾语补足语和主语补足语。是对宾语和主语的补充说明,与其有主动或被动的逻辑关系。
例如:You should keep the room clean and tidy.
你应该让屋子保持干净整洁。
(You是主语, should keep是谓语,the room是宾语,clean and tidy是宾语补足语。)
This kind of food tastes delicious.
这种食物吃起来很可口。
(This kind of food是主语, tastes是系动词, delicious是表语。)
注意:主语、谓语、宾语、系动词、表语、补语是一个句子的主干成分;定语和状语是一个句子的修饰性成分。
求一个英语句子成分分析
I had to think of a way of preventing...(省略)
这句话意为:我必须想出一个阻止……的办法。
这个句子中I是主语,had to是一个情态动词,think of是一个短语动词,他们一起构成句子的谓语,其中think of是一个习语,不能分开来解,就像look after“照顾”,look for"寻找”等短语动词是一样的;a way of preventing …是这个句子的宾语。
呵呵,其实我觉得初中英语我还是有发言权的,特别是英语的句子成分。建议你再好好的看看这个句子,再评说我给你的解答。我相信学无止境!听君一席话,我也准备去研究研究这个问题。
补充一点:a way of preventing……这个短语中,of preventing……做的是a way的定语,再细点preventing做的是of的宾语。
初中英语句子成分分析
句子的组成部分,包括主语、谓语、宾语、定语、补语、状语、表语七种
主语是句子叙述的主体,可由名词、代词、数词、名词化的形容词、不定式、动名词和主语从句等来承担。
谓语说明主语所发出的动作或具有的特征和状态。谓语由动词来承担。
宾语是动作的对象或承受者,常位于及物动词或介词后面。宾语可由名词、代词、数词、名词化的形容词、不定式、动名词、宾语从句等来担任。
主语和谓语是英语句子的两大成分,除少数句子(如祈使句和感叹句等)外,一句话必须同时具有主语和谓语所表达的意思才能完整。主语是针对谓语而言的,是一句话的主题,谓语用来说明主语的情况,为主语提供信息。例如:They are working.主语是they(他们),那麽他们在做什麽呢?看来没有谓语are working 是不行的。在正常情况下,英语的主语和谓语的位置与汉语一致,也就是说主语在前,谓语紧跟其后。那麽,哪些词语可以做主语,谓语,何时主谓倒置,主语与谓语的一致情况如何,我将一一讲述。
一、哪些词可以充当主语
1,名词
例如: A mooncake is a delicious, round cake.
The first truck is carrying a few baskets.
The temperature will stay above zero.
The doctor looked over Mrs. Brown very carefully.
China does not want to copy the USA’s example.
2,代词
例如: It’s a young forest.
I don’t know if it will grow.
That’s a bit expensive.
You’d better buy a new pair.
I’m afraid we hen’t got any black shoes.
3,数词
例如:One and two is three.
One is not enough for me. I want one more.
One of them is English.
Suddenly one of the bags fell off the truck.
Two will be enough.
4,不定式 (常以 It’s adj. to do sth. 形式出现)
例如: To give is better than to receive =Its better to give.
I found it difficult to get to sleep.
It’s glad to see you again.
It was difficult to see.
But it’s good to swim in summer.
5,IT 作主语,有如下情况:
1)指代刚刚提到的事物:What’s this ? It’s a bus. (指代what)
2)指代一个你不知道或判断不清性别的人:Who’s knocking the door? It’s me. (指代 who)
Who’s the baby in the picture? It’s my sister. (指代 who)
3) 表示时间,天气,距离:
What’s the time? It’s eight o’clock. (时间)
What’s it going to be tomorrow? It’s going to be rainy.(天气)
How far is it? It’s about one kilometre away. (距离)
6. THERE 引起的There be 句型中,be 作谓语,主语位居其后。如:
There are many different kinds of mooncakes.
There will be a strong wind.
二、谓语
谓语有动词构成,依据其在句中繁简程度可把谓语分为简单谓语和复合谓语两类。不论何种时态,语态,语气,凡由一个动词(或动词词组)构成的谓语都是简单谓语。例如:
I like walking.(一般现在时主动语态)
I made your birthday cake last night. (一般过去时主动语态)
It is used by trellers and business people all over the world. (一般现在时被动语态)
复合谓语也可分为两种情况:
第一种是由情态动词,助动词+不带to的动词不定式构成的复合谓语:
What does this word mean?
I won’t do it again.
I’ll go and move away the bag of rice with Lin Tao.
You’d better catch a bus.
第二种是由连系动词+表语构成的复合谓语。例如:
You look the same.
We are all here.
The weather gets wamer, and the days get longer.
Keep quite and listen to me.
He looked worried.
We he to be up early in the moming.
Is Bill in?
School Is over. Let’s go home.
My pen is in my bag.
I feel terrible.
I* fell tried all the time.
He seemed rather tired last night.
连系动词和表语在意思上紧密联系,不宜分割;有关动词的种类这方面知识在课本中已有介绍,此处不多说了。
三、主语与谓语的一致
英语句子的主语和谓语的一致性,是英汉两种语言的区别之一。具体说来有如下特征:
1, 谓语动词在人称和数上应与主语保持一致。如:
Now the teacher comes into the classroom.
本句属一般现在时,主语the teacher 为第三人称单数,因而谓语动词come 应加s.
One morming she was working at her desk in the library wher a boy came in. 本句属主从复合句,主句用过去进行时,从句为一般过去时;主句中主语she为第三人称单数,所以谓语为 was working.
1) 主语含有 and 时,如表示一个单一的概念,谓语动词常用单数(特别是当and 连接的是两个不可数名词时),否则用复数。如:
One and three is four. And 前后均为数字,表示同一个概念,谓语动词应用is.
Tea and milk is my fourite drink. 本题中tea and milk 指一种饮料,故谓语用is。
Tom and Li Lei are my best friends. Tom 和 Li lei 是完全不同的两个人,有不同的特征,因而谓语是are。
2) 主语为动词不定式时,其谓语常用单数形式。如:
To give is better than to receive.
It was difficult to see.
It’s best to wear cool clothes.
同样,动名词作主语,谓语动词也为单数。初中阶段只学了一句:
It (playing) is much better than hing classes.
3) 不可数名词作主语,谓语动词视为单数。如:
The best time to come to China is autumn.
The weather in England never gets too hot.
4) 在姓的复数前加the 表示一家人,谓语动词为复数。如:
What time do the Reads he breakfast? 主语是the Reads, 表示里得一家人,谓语动词用do….he.
5) 表示时间的复数名词作主语,常作整体看待,其谓语动词为单数形式。如:
Two months is quite a long time.
6) “几加几等于几”的算式中,谓语动词常为单数。如:
Twenty and forty is sixty.
主 谓
7) 某些表示学科的名词作主语,无论其结尾是什麽,谓语动词都视为单数。如:
Maths is my fourite subject.
主 谓
8) each 以及由some,any,no,every 构成的复合代词作主语,谓语动词为单数。如:
There’s something wrong with my ears!
谓 主
Everyone is going into class.
主 谓
9) what,who which 等词做主语,谓语动词形式视意思而定。如:
What is this?(this 为单数,用is)
What are these? (these 为复数,用are )
Which is your friend? 哪一个人是你的朋友?
Which are your friends? 哪些人是你的朋友?
10) None 作主语,其谓语可以是单数,也可以是复数,此项目并非初中阶段重点,故此不谈。
11) People,Chinese, Japanese 作主语,谓语动词为复数。如:
There are four people in my family.
谓 主
The chinese people are very friendly.
12) population 作主语,指“人口”时,谓语为单数;其前有表示数量的修饰语时,谓语为复数;课本第三册只要求掌握作“人口”讲时谓语的情况:
What’s the population of Germany?
谓 主
What was the population of the world in 1950?
谓 主
Half of the population of China are women.
修饰语 主 谓
2, 由 either …or 或neither …nor 连接的两个并列成分作主语,其谓语动词形式与后一个主语保持一致。如:Either Lily or Lucy is going to come.(Lily和Lucy 谁去都行。后一个主语Lucy 为第三人称单数,谓语用is going to come.)
Either I or he does well in English. 我和他的英语都不错。
Neither I nor she likes swimming. 我和她都不喜欢游泳。
由these 和here 引出的含有不只一个主语的句子,其谓语动词形式由最靠近谓语的主语形式决定。如:
These is a pen, two rulers and three books on the desk.
Here are some cups,a glass and some pears on
句子的成分:
构成句子的基本成分叫做句子成分。句子成分可分为主语,谓语,宾语,表语,定语,状语,同位语。它们可以由单词来担任,也可以由词组,以及句子来担任。
主语
主语是一个句子中所要表达,描述的人或物,是句子的主体。
I work here.
我在这儿工作。
She is a new teacher.
她是一个新教师。
主语可以由名词,代词,数词,动词不定式,动名词,名词化形容词,分词,从句,短语等来担任。
The book is on the desk.
书在桌子上。
I get an idea.
我有一个主意。
Two and two are four.
二加二等于四。
When to be ginisnotknownyet.
什么时间开始还不知道。
What I know is important.
我所知道的很重要。
谓语谓语是用来说明主语做了什么动作或处在什么状态。谓语可以由动词来担任,一般放在主语的后面。
We don't know him very well.
我们不太了解他。
She speaks English fluently.
她英语讲得很流利。
表语表语是用来说明主语的性质,身份,特征和状态。表语须和连系动词一起构成句子的复合谓语。表语一般放在系动词之后。表语可以由名词,形容词或起名词和形容词作用的词和短语担任。
These desks are yellow.
这些桌子是**的。
I am all right.
我没事。
We are hy now.
我们现在很幸福。
It's over.
时间到了。
She is ten.
她十岁了。
My work is teaching English,
我的工作是教英语。
The dictionary is in the bag.
词典在书包里边。
My question is how you knew him.
我的问题是你如何认识他的。
宾语
宾语是谓语动作所涉及的对象,它是动作的承受者,宾语可以由名词或起名词作用的成分担任,宾语一般放在谓语动词后面。
I saw a cat in the tree.
我看见树上有一只猫。
I want to go shopping.
我想去买东西。
He said he could be here.
他说他会来的。
We think you are right.
我们认为你是对的。
有些及物动词可以有两个宾语,其中一个宾语多指人,另一个宾语指物,指人的宾语叫做间接宾语,指物的宾语叫做直接宾语,可以带两个宾语的动词有 bring,give,show,send,pass,tell等。间接宾语一般放在直接宾语的前面,如果强调直接宾语可把直接宾语放在间接宾语的前面, 但间接宾语前须加"to"。
My father bought me a book.
我父亲给我买了一本书。
Give the rubber to me.
把橡皮给我。
Please give the letter to XiaoLi.
请把这封信给小李。
有些及物动词除跟一个宾语外,还需要加上宾语补足语,否则意思不完整,它们一起构成复合宾语,复合宾语中宾语和后面的宾语补足语有一种逻辑上的主谓关系,这也是判断是两个宾语还是复合宾语的依据,宾语可以由名词或起名词作用的词担任。
We all call him LaoWang.
我们都叫他老王。
Please color it red.
请给它涂上红颜色。
We found the little girl in the hill.
我们在山上找到了小女孩。
定语用于描述名词,代词,短语或从句的性质,特征范围等情况的词叫做定语,定语可以由名词,形容词和起名词和形容词作用的词,短语担任。如果定语是单个词,定语放在被修饰词的前面,如果是词组,定语放在被修饰词的后面。
That is a beautiful flower.
那是一朵漂亮的花。
The TV set made in that factory is very good.
那个工厂生产的电视机很好。
This is my book,not your book.
这是我的书,不是你的书。
There are more than twenty trees in our
school.
我们学校里有二十多棵树。
I he a lot of things to do.
我有好多要做的事情。
Our country is a developing country.
我们的国家是一个发展中的国家。
状语:说明事物发生的时间,地点,原因,目的,结果方式,条件或伴随情况,程度等情况的词叫状语。状语可以由副词,短语以及从句来担任。
同位语: 当两个指同一事物的句子成分放在同等位置时,一个句子成分可被用来说明或解释另一个句子成分,前者就叫做后者的同位语(ositive).这两个句子成分多由名词(代词)担任,同位语通常皆放在其说明的名词(代词)之后。
词类和句子成分的关系初中英语知识点梳理
掌握英语 句子 结构,才能更准确的理解英语句子的意思并正确写出,也有利于提高中学生的 英语阅读 能力和写作水平。下面是我带来的初中英语句子成分,欢迎阅读!
初中英语句子成分精选
初中英语句子成分分析与讲解
英语句子与汉语句子一样,都是由单词按照一定的规则所组成的。不同的词类在句中所起的作用是不同的。因此,只有搞清不同词类在句中可充当哪些成分,才能正确分析、理解句子的含义,并能准确地遣词 造句 ,逐渐达到流利地说出地道的英语。
请同学们认真阅读下面的问答,我相信它一定会对同学们起到抛砖引玉的作用。
问什么是句子成分?英语句子包含哪些成分?
答组成句子的各个部分叫做句子成分。它包括:主语、谓语、宾语、定语、状语、表语和宾语补足语等。
问各成分在句中的作用如何?分别由哪些词及 短语 充当?
答
1.主语:是句子要说明的人或事物,是句子的主体,一般由名词、代词、数词、不定式或动名词等充当。如:
The car is running fast.(名词)
We are students.(代词)
One of my classmates is from Shanghai.(数词)
It's bad manners to spit in public.(不定式)
Eating too much is bad for your health.(动名词)
注意若不定式短语作主语常用it作形式主语,而把真正的主语(不定式短语)放在句后。
2.谓语:说明主语的动作或状态,也是句子的主体部分,一般由动词充当。动词分为实义动词、连系动词、情态动词和助动词。实义动词单独作谓语,连系动词与表语一起构成谓语,情态动词与省略to的不定式构成合成谓语,助动词与动词原形共同构成谓语部分。如:
He works in a factory.(实义动词)
I felt cold.(系动词+表语)
How can I get to the station?(情态动词+实义动词)
Do you speak English?(助动词+实义动词)
They are working in a field.(助动词+实义动词)
注意谓语与主语在人称与数方面要相互照应。
3.宾语:是及物动词所涉及的对象,一般由名词、代词、不定式及动名词等充当。如: He is doing his homework.(名词)
They did nothing this morning.(代词)
She wants to go home.(不定式)
We enjoy playing football.(动名词)
注意①有的动词可接双宾语,间接宾语指人,直接宾语指物。这类动词常见的有:give,buy,lend,pass, tell,lee等。如:
He bought me a book.
Pass me the ball,will you?(间宾+直宾)
直接宾语一般放在间接宾语之后,但若把直接宾语放在前面,则要在间接宾语前加适当的介词如to或 for等。如:
Han Chen lent some money to Li Hai.(直宾+间宾)
Xiao Liu bought a dictionary for Tom.(直宾+间宾)
②有的动词常用不定式作宾语,而不能用动名词。这类动词有:want,wish, hope,promise,decide,agree, choose,care等。如:
I hope to see you again.
③有的动词一般只用动名词作宾语,而不用不定式。这类动词有:enjoy,finish,mind,practise,miss, suggest,keep(on)等。如:
Do you mind my opening the window?
④有的动词后接不定式与动名词含义不同。
a)forget to do表示?未发生的动作?,forget doing表示?已完成的动作?。如: Don't forget to come here earlier tomorrow.(还没来)
I forgot returning the book to him.(书已还给他了)
b)stop to do(不定式为状语)表示?停下
原来的事,去做另一件事?,stop doing表示?停止做某事?。如:
I stopped to talk with him.(我停下来与他谈话。)
The students stopped talking when the teacher came in.(老师进来时学生们停止谈话。)
4.定语:用于修饰名词或代词,一般由形容词、名词、数词、不定式等充当。如: What a beautiful kite it is!(形容词)
She is a chemistry teacher.(名词)
There are two students in the classroom.(数词)
We he something to do tomorrow.(不定式)
The man in blue is my brother.(介词短语)
注意定语一般位于被修饰词之前,但若修饰不定代词或不定式等短语作定语,则放在后面。
5.状语:用于修饰动词、形容词、副词或全句,一般由副词、介词短语、不定式短语或从句充当。单个副词作状语一般放在被修饰词之前,短语或从句放在句首或句末。如:
Thank you very much.(副词)
I get up at five in the morning.(介词短语)
He is studying hard so as to catch up with others.(不定式短语)
We were hing breakfast when the telephone rang.(从句)
注意enough作状语只能放在被修饰词之后。如:
He is old enough to go to school.
6.表语:用于说明主语的身份、特征或感受,一般由名词、数词、形容词、分词等充当。常用的连系动词有:be,look,get,sound(听起来),feel,become, smell,turn,taste(尝起来)等。如:
They are workers.(名词)
Two and three is five.(数词)
The story is very interesting.(形容词)
M y job(工作)is teaching English.(动名词)
She is at home.(介词短语)
I feel terrible.(形容词)
The dish tastes delicious.(形容词)
7.宾语补足语:用于补充说明宾语的动作,一般位于宾语之后,宾语与宾语补足语一起构成复合宾语。需接复合宾语的动词有:tell,let,help,teach, ask,see,he,order,make等。?宾补?一般由不定式短语、分词、名词、形容词等充当。如:
We elected him monitor.(名词)
I found it difficult to learn English well.(形容词)
The doctor told me to do more exercise.(不定式短语)
He is going to he his hair cut.(过去分词)
They saw a bird flying in the sky.(现在分词)
初中英语句子成分学习
英语句子成分结构详解
一、英语语句基本结构分析:
(一)主谓宾结构:
1、主语:可以作主语的成分有名词(如boy),主格代词(如you),数词,动词不定式,动名词等。主语一般在句首。注意名词单数形式常和冠词不分家!
eg: The boy comes from America.
He made a speech.
Two and two is four.
To be a teacher is my dream.
Doing a research is a necessary step of covering a story.
2、谓语:谓语由动词构成,是英语时态、语态变化的主角,一般在主语之后。谓语可以是不及物动词(vi.)没
有宾语,形成主谓结构,
eg:We come.
Many changes took place in my home town.
注(以下这些词是不及物动词:表发生、出现的,如:take place, ear, hen, break out; 表来、去,如:come, go 等)
3、宾语:宾语位于及物动词之后,一般同主语构成一样,不同的是构成宾语的代词必须是?代词宾格?,如:me,him,them等。除了代词宾格可以作宾语外,名词,动名词,不定式等可以作宾语。
eg:I will do it tomorrow.
The boy needs a pen.
I like swimming.
I like to swim this afternoon.
(二)主系表结构:
1、主语:同?主谓宾?结构。
2、谓语:联系动词(Link verb):be动词(am,is,are,was,were,he been);其他联系动词如:become成为,turn变成,go变和感官动词如:feel, touch, hear, see等。其特点是联系动词与其后的表语没有动宾关系,表语多为形容词或副词,既,不可能是宾语。
3、表语:说明主语的状态、性质、等。可为形容词、副词、名词、代词、不定式、分词。
(1)当联系动词不是be,而其后是名词和代词时,多表达?转变为?之意,注意与动宾关系的区别。
eg: He became a teacher at last.
His face turned red.
(2)感官动词多可用作联系动词
eg: He looks well.他面色好。
It sounds nice.这个听起来不错。
I feel good.我感觉好。
The egg smells bad.这个鸡蛋难闻。
例:Tom is a boy.(Tom是个男孩)主语为Tom,系词为be动词的第三人称单数is,表语为a boy
(三)There be 结构:
There be 表示?存在有?。这里的there没有实际意义,不可与副词?there那里?混淆。 此结构后跟名词,表示?(存在)有某事物?
试比较:There is a boy there.(那儿有一个男孩。)/前一个there无实意,后一个there为副词?那里?。
二、定语
定语是对名词或代词起修饰、限定作用的词、短语或句子,汉语中常用的?表示。 定语通常位于被修饰的成分前。若修饰some,any,every,no构成的复合不定代词时,(如:something、nothing);或不定式、分词短语作定语、从句作定语时,则定语通常置后。副词用作定语时须放在名词之后。
(一)形容词作定语:
The little boy needs a blue pen.小男孩需要一支蓝色的钢笔。
(二)数词作定语相当于形容词:
Two boys need two pens.两个男孩需要两支钢笔。
(三)形容词性物主代词或名词所有格作定语:
His boy needs Tom's pen.他的男孩需要Tom的钢笔。
There are two boys of Toms there.那儿有Tom家的两个男孩。
(四)介词短语作定语:
The boy in the classroom needs a pen of yours.教室里的男孩需要你的一支钢笔。 The boy in blue is Tom.穿兰色衣服的孩子是汤姆。
There are two boys of 9,and three of 10.有两个9岁的,三个10岁的男孩。
(五)名词作定语:
The boy needs a ball pen.男孩需要一支圆珠笔。
副词作定语:
The boy there needs a pen.那儿的男孩需要一支钢笔。
不定式作定语:
The boy to write this letter needs a pen.写这封信的男孩需要一支钢笔。
(六)分词(短语)作定语:
The smiling boy needs a pen bought by his mother.那个微笑的男孩需要一支他妈妈买的钢笔。
(七) 定语从句:
The boy who is reading needs a pen.那个在阅读的男孩需要一支钢笔。
三、状语
状语修饰动词、形容词、副词或全句,说明方式、因果、条件、时间、地点、让步、方向、程度、目的等
状语在句子中的位置很灵活,常见情况为:通常在句子基本结构之后,强调时放在句首;修饰形容词或副词时,通常位于被修饰的词之前;表示时间、地点、目的的状语一般位于句子两头,强调时放在句首,地点状语一般须在时间状语之前;一些表示不确定时间(如:often)或程度(如:almost)的副词状语通常位于be动词、助动词、情态动词之后,动词之前。
有时状语在句中的某个位置会引起歧义,应注意,如:The boy calls the girl in the classroom.一般理解成?男孩喊教室里的女孩?(此时in the classroom为girl的定语),也可以理解为?男孩在教室里喊女孩(此时?in the classroom为地点状语),最好写作?In the classroom,the boy calls the girl.'
(一)副词(短语)作状语:
The boy needs a pen very much.男孩非常需要一支钢笔。(程度状语)
The boy needs very much the pen bought by his mother.男孩非常需要他母亲买的那支钢笔。(宾语较长则状语前置)
The boy needs a pen now./Now,the boy needs a pen./The boy,now,needs a pen./男孩现在需要一支钢笔。(时间状语)
(二)介词短语作状语:
In the classroom,the boy needs a pen.在教室里,男孩需要一支钢笔。(地点状语) Before his mother,Tom is always a boy.在母亲面前,汤姆总是一个男孩子.(条件状语) On Sundays,there is no student in the classroom.星期天,教室里没有学生.(时间状语)
(三)分词(短语)作状语:
He sits there,asking for a pen.他坐在那儿要一支笔。(表示伴随状态)
Hing to finish his homework,the boy needs a pen.因为不得不完成作业,男孩需要一支笔。(原因状语)
(四)不定式作状语:
The boy needs a pen to do his homework.男孩需要一支笔写家庭作业。(目的状语)
(五)名词作状语:
Come this way!走这条路!(方向状语)
(六)状语从句:
时间状语从句,地点状语从句,原因状语从句,结果状语从句,目的状语从句,比较状语从句,让步状语从句,条件状语从句
四、直接宾语和间接宾语:
(一)特殊的同源宾语现象: fight a fight , dream a dream , etc.
(二)有些及物动词可以有两个宾语,如:give给,pass递,bring带,show显示。这两个宾语通常一个指人,为间接宾语;一个指物,为直接宾语。间接宾语一般位于直接宾语之前。
一般的顺序为:动词 + 间接宾语 + 直接宾语。
eg:Give me a cup of tea,please.
强调间接宾语顺序为:动词 + 直接宾语 + to + 间接宾语。eg:Show this house to Mr.Smith.Mr.
五、宾语补足语
位于宾语之后对宾语作出说明的成分。宾语与其补足语有逻辑上的主谓关系,它们一起构成复合宾语。
(一)名词/代词宾格 + 名词
The war made him a soldier.战争使他成为一名战士.
(二)名词/代词宾格 + 形容词
New methods make the job easy.新 方法 使这项工作变得轻松.
(三)名词/代词宾格 + 介词短语
I often find him at work.我经常发现他在工作.
(四)名词/代词宾格 + 动词不定式
The teacher ask the students to close the windows.老师让学生们关上窗户.
(五)名词/代词宾格 + 分词
I saw a cat running across the road.我看见一只猫跑过了马路.
六、同位语
同位语是在名词或代词之后并列名词或代词对前者加以说明的成分,近乎于后置定语。如: We students should study hard. (students是we的同位语,都是指同一批?学生?) We all are students. (all是we的同位语,都指同样的?我们?)
七、独立成分
有时句子中会有一些与句子没有语法联系的成分,称为句子独立成分(注意:区别于分词独立结构)。
感叹词:oh,hello,aha,ah,等。肯定词yes否定词no称呼语:称呼人的用语。插入语:一些句中插入的 I think , I believe,等。
如: The story,I think,has never come to the end./我相信,这个 故事 还远没结束.
情态词,表示说话人的语气(多作为修饰全句的状语):perhaps也许,maybe大概,acturely实际上,certainly当然,等。
八、分词独立结构
分词作状语时其逻辑主语与句子的主语一致! 否则应有自己的逻辑主语,构成分词独立结
构。
例:错句:Studying hard,your score will go up.
正确:(1) Studying hard,you can make your score go up. 或 (2)If you study hard,your score will go up.
解析:错句中分词studying没有自带逻辑主语,则其逻辑主语就是句子的主语,既your score . 显然做study的应是人,不应是your score(分数). 正确句(1)更正了句子的主语,使其与分词逻辑主语一致( 同为you );正确句(2)则使用条件分句带出study的主语,(不过已经不是分词结构了).
分词独立结构常省略being,hing been.不过?There being...?的场合不能省略.
如:
Game (being) over,he went home.
He stands there,book (being) in hand.
独立结构还可用with、without引导,作状语或定语。这种结构不但可以用分词,还可以用不定式、形容词、介词短语、副词或名词等。
如:
With nothing to do,he fell asleep soon.无事可做,他很快就睡着了。
The teacher came in,with glasses on his nose.老师进来了,戴着一付眼镜。(注意,此句on his nose不可省略!)
初中英语句子成分分析法
1.谓语: 说明主语的动作和状态。动词在句中作谓语,一般放在主语之后。例如:
1)The new term begins on September 1st .(行为动词作谓语)
2)She seems tired. (连系动词作谓语)
3)He has gone to Beijing. (行为动词作谓语)
2.宾语: 及物动词涉及的人或物称为动词宾语。宾语一般放在及物动词(或相当于及物动词的短语)后。介词后的名词或代词称为介词宾语。名词、代词在句中常作宾语。此外,动词不定式、动名词和从句也可作宾语。例如:
1)Wang Ling lent me a novel. (代词me作间接宾语;名词a novel作直接宾语)
2)The medicine is good for a cough. ( 名词a cough作介词宾语)
3)My little sister always likes to ask questions. (不定式to ask questions作动词likes 的宾语)
4)His brother is good at playing chess. (动词名词playing chess作介词宾语)
5)Would you mind coming earlier tomorrow? (coming作动词宾语)
3.宾语补足语(复合宾语的第二部分): 在宾语后补充说明宾语的动作、状态、特征的成分称为宾补。名词、形容词、动词不定式和动名词可作宾补。(见前面简单句的`五种基本句型五)
4.表语: 在连系动词后用来说明主语的身份、状态或特征的成分是表语。可作表语的有:名词、代词、形容词、介词短语、不定式、动名词以及表语从句。(参见简单句的五种基本句型三)
请大家告诉我初中英语的特殊句式(宾语从句)啊这一类的。
英语句子是英语对话和文章的基础。下面是我带来的初中英语句子成分分析,欢迎阅读!
初中英语句子成分分析精选
句子是由各种词类按照一定的语法规则组成的,可以表达完整的概念。句子开头第一个字母一定要大写,结尾要注明标点符号。
一、句子的成分
组成句子的各个部分叫作句子的成分。句子的成分有主语、谓语、表语、宾语直接宾语和间接宾语、宾语补足语、定语和状语。其中主语和谓语是句子的主体,表语、宾语和宾语 补足语是谓语的组成部分,其他成分如定语和状语是句子的次要部分。
1 主语 表示所说的“是什么”或“是谁”,通常用名词、代词、不定式或相当于名词的词、短语或从句担任。主语要放在句首。
To say is one thing, and to do is another. 说是一回事,做是另一回事。不定式作主语 What you said hurt me badly. 你所说的话深深地刺伤了我。从句作主语
2 谓语 起著说明主语的动作、特征或状态的作用,必须用动词表示。谓语和主语在人称和数两方面要一致,通常在主语之后。谓语通常有三个表现形式:
1动词或动词短语作谓语
He studies hard. 他学习很努力。 The performance has already begun.演出已经开始。
2谓语动词和宾语及宾语补语作谓语
They are picking les. 他们正在摘苹果。 He made us laugh heily.他使我们大笑不止。
3连系动词和表语作谓语 Her mother is an inspector. 她的母亲是一位检查官。
It is getting dark. 天色渐渐地黑了下来。
He is feeling well. 他现在感觉身体很好。
句子成分巧划分 :主在前,谓在中,宾语、状语后面冲。短语定语主宾后,形、代定语主宾前。间宾直宾紧相依,直、间之间to、for连,宾补位于宾语后,地状常在时状前。
3 表语 用于说明主语的性质、特征、身份或状态,可以由名词、形容词、副词、介词和不定式 以及相当于名词或形容词的词或短语来担任,表语要放在连系动词之后。
Her job is to wash all the sheets and the clothes. 她的工作是洗这些床单和衣服。不定式作表语 Teaching is learning. 教学相长。动名词作表语
4 宾语 是及物动词所示动作的物件或介词的物件,由名词、代词、不定式或相当于名词的词、 短语及从句都可以担任作宾语。宾语要放在谓语动词及物动词或介词之后。
Do you enjoy living here? 你愿意住在这里吗? 动名词作宾语
I want only one. 我只要一个。数词作宾语
I don't think you are right. 我认为你不对。从句作宾语
注意:①某些及物动词之后要求有双宾语即直接宾语和间接宾语, 直接宾语指物,间接宾语指人。这一类动词有:bring, give, pass, tell, hand, show, s end, read, lee, teach, find, buy, make, do, get, order, play, sing, pay等。
She showed me a few magazines. 她拿出了一些杂志给我看。
I promised her a wonderful present on her birthday .我答应在她生日那天给她一件奇妙的礼物。
②在需要的情况下,间接宾语也可以位于直接宾语之后,但此时间接宾语之前需要加介词。 She made me a sweater. She made a sweater for me. 她给我织了一件毛衣。
He left her three children. He left three children to her 他给她留下三个孩子。
③有些及物动词的后面,其宾语还需要有一个补足语,才能表达完整的意思。这样的宾语和宾语补足语称为复合宾语。名词、形容词、不定式或介词短语都可以作宾语补足语。
The couple named the baby Mary.名词作宾 补 这对夫妻给孩子取名叫玛丽。
He made her unhy. 他使她很不高兴。形容词作宾补
“Let me out!” The boy cried. “让我出去!”那男孩喊道。副词作宾补
She saw a man in front of the gate. 她看见门外有一个男人。介词短语作宾补
She often helps me do the housework. 她经常帮助我做家务。不定式作宾补
I kept you waiting for half an hour. 我让你等了半个小时。动名词作宾补
5 状语
状语用于修饰动词、形容词、副词或整个句子。通常表示行为发生的时间、地点、目的、方 式、程度等。状语一般由副词、介词短语、分词和分词短语、不定式或相当于副词的词或短 语来担当。其位置一般放在句末,但也可放在句首或句中。
She drove fast.副词作状语 她把车开得飞快。
There is a shelter under the post office.
在邮局的地底下,有一个掩蔽所。介词短语作状语
To liberate our country, they devoted their lives.
为了解放祖国,他们献出了生命。不定式短语作状语
Seeing his old mother, the man went towards her and threw himself on his knees.
那人一看见年迈的母亲就跑上前去跪倒在她面前。分词短语作状语
It was blowing hard when she was on her way home yesterday.
昨天她回家的路上,风刮得正大。从句作状语
6 定语
定语用于修饰名词或代词。可以担任定语的有形容词、代词、名词、数词、名词所有格、副 词、不定式、分词和分词短语、介词短语及从句等等。定语的位置很灵活,凡有名词和代词 的地方都可以有定语。
The man outside the teacher's office is his father.办公室外面的那人是他的父亲。介词短语作定语 I'll he a lot of clothes to wash this Saturday. 这个星期六我要洗好多衣服。不定式作定语 Will you say something about your trelling experience? 动名词作定语
The woman who is singing on the stage is her aunt.从句作定语正在台上演唱的那女人是她姑姑。
二、句子的种类
一、简单句
简单句只包含一个主谓结构,并且各个结构都是由单词或短语组成,不包含任何从句。有五种基本句型。
1.主语+谓语不及物动词
The new term begins. 新学期开始了。
2.主语+谓语及物动词+宾语
The girl is learning to play the piano. 这个女孩在学弹钢琴。
3.主语+连系动词+表语
The rice got burned。 饭焖煳了。
4.主语+谓语及物动词+间接宾语+直接宾语
He bought her a watch. 他给她买了一块表。
5. 主语+谓语及物动词+宾语+宾语补语
We all believed you honest. 我们都认为你是诚实的。
二、并列句简单句+连词+简单句
并列句是由两个或多个简单句连线而成的。其中的各个简单句并列平行,同等重要,相互之 间没有从属关系,能够独立成句。它们之间要用连词连线。并列句可分为四种:
1.表示相同关系 用连词或逗号、分号连线构成并列句。常用连词有:and, not only...but also..., neither...nor...
Susan not only runs fast, but also jumps high. 苏姗不但跑得快,而且跳得高。
I could neither swim nor skate. 我既不会游泳,也不会滑冰。
2.表示转折关系 常用连词有:but, still, yet, while等。
It was late at night, but he went on doing his homework.夜已深了,但是他还在继续做作业。
She was busy cooking while they were watching TV.她忙着做饭,而他们却在看电视。
The film is not perfect, still, it's good.这部影片虽然不是无可挑剔,但还是好的。
3.表示选择关系 常用连词为:or, either...or...。
The teacher wanted to see either his father or mother.老师要见一下他的父亲或是母亲。
Either this road or that on e can lead you to that hospital.这条路或那条路都通往那家医院。
Hurry up,or you'll miss the train.
4.表示因果关系 常用连词有for和so。
We hurried to the railway station, for there was little time for the train to lee.
我们急忙赶往车站,因为火车很快就要开了。
The teacher asked Susan to go, so she went did.老师让苏姗到她那去,因此她就去了。
三、复合句主句+连词+从句
包含一个主句,一个或一个以上的从句的句子叫复合句。从句从属于主句并充当主句的某一成分,如主语,表语,宾语,定语,状语等。中考主要考宾语、定语、状语从句。注意引导词、语序和时态。
初中英语句子成分分析练习
巩固练习 同义句转换
1.There is only a chair in the room.同义句转换
There is _________ _________a chair in the room..
2. Mrs.Smith is busy. She is doing her housework now.
Mrs.Smith is_________ _________ her housework now.
3.The teacher said,“Don’t cheat in exams,children!”
The teacher told the children _________ _________ cheat in exams.
4.Nick was so tired that he couldn’t walk any further. 全品中考网
Nick was _____________________________ any further.
5.We can’t finish the project on time unless you support us.
The project can’t be finished on time ______________________________.
6.Shall we watch the exciting ping-pong match together?
______________________________watch the exciting ping-pong match together?
7.My cousin usually walks to school every morning. 改为同义句
My cousin usually goes to school _________ _________ every morning. 对划线部分提问
__________ _________is your friend?
9. “Are you going to visit Zi Gong next Week?”Father asked me.改为间接引语
Father asked me __________I________going to visit Zi Gong next week. 对划线部分提问
___________ _________you use to stay on family holidays?
11.James spent ten years making this amazing film保持句意基本不变
__________ _________James ten years to make this amazing film.
12.Chris has gone to South Africa to enjoy the 2010 World Cup.
Karen has gone to South Africa to enjoy the 2010 World Cup, too. 合并为一句
_________Chris _________Karen he gone to South Africa to enjoy the 2010 World Cup.
13.Visitors love this city because it has historical sights and delicious food.改为简单句
Visitors love this city__________ _________its historical sights and delicious food.
14. 对划线部分提问
___________________from Fukang to Unmnqi by bus? 对划线部分提问
_______________this new puter __________________?
16、不同句子结构的转换,主要指简单句、并列句和复合句间的转换
1We found him a good pupil. We found _______ ______ _______ a good pupil.
2The room is so *** all that my family can't live in it.
The room isn't ______ _______ ____ my family ___ live in.
The room is ______ *** all ________ my family _______ live in.
3His grandfather died ten years ago. It ____ ten years ___ his grandfather ______ .
4I'm not sure what I should do next. I'm not sure _____ ___ ____ next.
5Hurry up, or you'll miss the train. ___ you ___ hurry up, you'll miss the train.
17、根据句意的转换
1 Yesterday everyone of us went to the farm except Lucy.
________ Lucy _______ go to the farm with us yesterday.
2Sam is friendly to his clas *** ates and his clas *** ates are friendly to him.
Sam _______ ______ well with his clas *** ates.
3Lily was born ten minutes earlier than I was. I am ten minutes _______ than Lily.
4English is spoken by the largest number of people in the world.
English _____ the largest number of ________ in the world.
5It's your turn to do it. It's _____ ____ you to do it.
6 It rained heily last night. There ______ _____ _____ last night.
7 The building is beautiful and there are many tall trees around it.
The building _____ many tall trees all _______ is beautiful.
8 I spent two hours reading the book yesterday.
_____ ______ me two hours ______ _____ the book yesterday.
9 He bought the book two weeks ago. He _____ _____ the book ____ two weeks.
10 You're very kind to help me with my maths.
___ __ very kind ___ you ___ help me with my maths.
11 My grandfather died ten years ago.
My grandfather ______ ______ ______ ______ ten years ago.
12 I think it is different from Chinese names. I don't think it is _____ _____ as Chinese names.
13 They planted millions of trees to se the farmland.
They planted millions of trees _____ _____ the farmland _____ ____ sed.
15The man thinks the same as I. The man ______ ______ me.
关于英语句子成分的问题!!!
因为已经看到有朋友为你讲述从句的问题了,讲解得很细致,所以我就不再解答了。但看到你追问的句子成分,我想将我手中的一点资料与你分享。
一、主要成分:
主语、谓语、表语、宾语、定语、状语、补语、同位语
1.主语
主语表示所说的“是什么”或“是谁”。能充当主语的词:名词、代词、数词、不定式、动名词或从句等。
数词: Four is enough for me. 四个对我来说就足够了。
Three and four makes seven.三加四等于七。
特殊情况
it 形式主语
例: It is our duty to try our best to learn English well.
It is very difficult for the young girl to carry the big box.
It is very kind of you to say so.
The +形容词(表一类)
例:The old need our help. 老人需要我们的照顾。
2.谓语
是“做什么”、“是什么”、“怎么样”。谓语主要指的动词(情态动词、连系动词、行为/实义动词、助动词)
助动词指的是:帮助完成时态、语态,或构成否定句、疑问句、简略回答等。主要有:be(is,am,are,was, were),do(does, did),he( has ,had),shall (should), will (would) 等。
行为/实义动词: 分及物动词(say)和不及物动词(talk) 、 延续性动词(keep)和瞬间性动词(borrow)、还有使役动词(make,he, let…)等
连系动词: be, look, seem, ear, smell, taste, sound, feel, keep,stay, become, get, go, turn, come, fall… (一般在使用连系动词时,会形成系动词+表语的结构。
3.表语
说明主语“是什么”或者“怎么样”。说明主语的特征、属性、状态和身份等。充当表语的可以是:名词、代词、数词、形容词、副词、不定式、doing 和done 、介词短语或从句等。
连系动词+… 就是系表结构。
4.宾语
宾语是及物动词所表示动作的对象或介词的对象,要放在谓语动词的后面或是介词后。
种类:直接宾语(动作的承受者)和间接宾语(动作是对谁或是为谁做的)例:Please give me(间宾) a glass of water(直宾).
可以做主语的词汇都可做宾语。
特殊:同源宾语 例:live a hy life laugh a good laugh 等。
5.定语
修饰名词或代词。一般由形容词、代词、数词、名词和名词所有格、doing 和done 等构成。放在前,形成前置定语。 例:my class。由形容词、副词、介词短语、动词不定式、doing 、done等,放在后,做后置定语。例:something interesting , the way to do …
从句也可以做定语,叫定语从句。一般放在所修饰的词汇后面,但也有放在前的情况。主要构成:先行部分+引导词+句子 例:I like the songs that I can sing along with.
6.状语
用来修饰动词、形容词、副词或整个句子。指时间、地点、方式、比较、程度、原因、目的、结果、条件和让步等。
副词、介词短语、动词不定式、分词短语、形容词短语和名词短语等可以充当状语。
例:Native speakers speak very fast.
7.补语
一般指宾语补足语。为了补充说明宾语的。两者在逻辑上是主谓关系,当含有宾语补足语的句子变为被动语态时,宾语补足语便是主语补足语。名词、形容词、副词、介词短语、doing、done、不定式等都可以做补足语。
例:I find watching English movies frustrating because they speak too quickly.
8.同位语
对句子中某一成分做进一步解释、说明, 与前面名词在语法上处于同等地位。常常置于被说明的词的后面。名词、代词、数词和从句都可以作同位语。
例:Shui junyi, a reporter from CCTV, is interviewing an important person.
We each he a new English book.
初中英语句子成分划分
in the meanwhile 同时
at the same time 同时
at noon(the morning, the evening, night)在中午(早上,晚上,半夜)
on time / in time 准时/及时
for a while一会儿
回答者:rockettosky - 门吏 二级 11-23 20:56
1. 人称代词
主格: I we you she he it they
宾格: me us you her him it them
形容词性物主代词:my our your her his its their
名词性物主代词: mine ours yours hers his its theirs
2.形容词和副词的比较级
(1) 一般在形容词或副词后+er
older taller longer stronger, etc
(2) 多音节词前+more
more interesting, etc.
(3) 双写最后一个字母,再+er
bigger fatter, etc.
(4) 把y变i,再+er
heier, earlier
(5) 不规则变化:
well-better, much/many-more, etc.
3.可数词的复数形式
Most nouns + s a book –books
Nouns ending in a consonant +y - y+ ies a story—stories
Nouns ending in s, sh, ch or x + es a glass—glasses a watch-watches
Nouns ending in o +s or +es a piano—pianos a mango—mangoes
Nouns ending in f or fe - f or fe +ves a knife –knives a shelf-shelves
4.不可数名词(单复数形式不变)
bread, rice, water ,juice etc.
5. 缩略形式
I’m = I am you’re = you are she’s = she is he’s = he is
it’s = it is who’s =who is can’t =can not isn’t=is not etc
6. a/an
a book, a peach
an egg an hour
7. Preposition:
on, in ,in front of, between, next to, near, beside, at, behind.
表示时间: at six o’clock, at Christmas, at breakfast
on Monday on 15th July On National Day
in the evening in December in winter
8. 基数词和序数词
one – first two-second twenty-twentieth
9. Some /any
I he some toys in my bedroom.
Do you he any brothers or sisters?
10. be 动词
(1) Basic form: am/are/is
(2) 肯定和否定句 I am(not) from London.
My eyes are(not) small.
My hair is(not) long.
(3)一般疑问句: Am I a Chniese? Yes, you are. No, you aren’t.
Are they American? Yes, they are. No, they aren’t.
Is the cat fat? Yes, it is. No, it isn’t.
11. there be 结构
肯定句: There is a …
There are …
一般疑问句:Is there …? Yes, there is./ No, there isn’t.
Are there…? Yes, there are. /No, there aren’t.
否定句: There isn’t …. There aren’t….
12. 祈使句
Sit down please
Don’t sit down, please.
13. 现在进行时.通常用“now”.
形式: be + verb +ing
eg: I am(not) doing my homework.
You/We/They are(not) reading.
He/She/It is(not) eating.
动词 —ing 的形式
Most verbs +ing walk—walking
Verbs ending in e -e + ing come—coming
Short verbs ending in a vowel + a consonant run –running swim—swimming
14 一般现在时。通常用 “usually, often, every day, sometimes”。
形式:
肯定句:
I go to school on foot every day.
She goes to school on foot every day.
在英语里的词性有如下这些:
1,名词,Nouns (n.) 表示人或事物的名称 box, pen,tree,le
2,代词,Pronouns (pron.)代替名词、数词、形容词We, this, them,myself
3,形容词, Adjectives(adj.) 用来修饰名词,表示人或事物的特征 good, sad, high, short
4,数词,Numerals(num.)表示数目或顺序 one,two, first
5,动词,Verb (v.) 表示动作或状态 Jump,sing,visit
6,副词,Adverbs(adv.) 修饰动、形、副等词,表示动作特征 there,widely,suddenly
7,冠词,Articles (art.) 用在名词前,帮助说明名词所指的范围 a, an, the
8,介词,Prepositions (prep.) 用在名词或代词前,说明它与别的词的关系 in,on,down,up
9,连词,Conjunctions (conj.) 表示人或事物的名称if,because,but
10,感叹词, Interjections (int.) 代替名词、数词、形容词等 oh,hello,hi,yeah
vt.是及物动词,vt.后必须跟宾语:sing a song
vi.是不及物动词,vi.后不直接带宾语或不带宾语:jump high
情态动词
情态动词,在英文中主要用来表示说话人的看法、态度等。它很接近中文里的能愿动词。从用法上来说,它有这样几个特点: 1)各个情态动词自身都有一定的词义。 2)情态动词不能在句中独立担当谓语。 3)情态动词在句中不受任何人称,性,数变化的影响。常见的情态动词如下:
can(could)
shall(should)/will(would)
may(might)
must
need
dare
ought(除这个是接to以外,以上各个词都是直接接动词原形)
1.主谓一致
1.1并列结构作主语时谓语用复数
例如:Reading and writing are very important. 读和写都是非常重要的。
[注意]: 当主语由and连接时,如果它表示一个单一的概念,即指同一人或同一物时,谓语动词用单数,and 此时连接的两个词前只有一个冠词。
例如:The iron and steel industry is very important to our life.钢铁工业对于我们的生活来说是非常重要的。
1.2主谓一致中的靠近原则
1)当there be 句型的主语是一系列事物时,谓语应与最邻近的主语保持一致。
例如:There is a pen, a knife and several books on the desk……桌上有笔、小刀和几本书。
2)当either… or… 与neither… nor, 连接两个主语时,谓语动词与最邻近的主语保持一致。
例如:Either you or she is to go.要么是你走,要么是她走。
Neither I nor he is to blame.我和他都不应该受责备。
1.3谓语动词与前面的主语一致
当主语后面跟有with, together with, like, except, but, no less than, as well as 等词引起的短语时,谓语动词与最前面的主语一致。
例如:The teacher together with some students is visiting the factory.老师和一些学生在参观工厂。
He as well as I wants to go boating.他和我都想去划船。
1.4谓语需用单数的情况
1) 代词each和由every, some, no, any等构成的复合代词作主语,或主语中含有each, every, 谓语需用单数。
例如:Each of us has a tape-recorder.我们每个人都有一台录音机。
There is something wrong with my watch.我的表出问题了。
2) 当主语是一本书或一条格言时,谓语动词常用单数。
例如:The Arabian Night is a book known to lovers of English.>是英语爱好者熟悉的一本好书。
3) 表示金钱,时间,价格或度量衡的复合名词作主语时,通常把这些名词看作一个整体,谓语一般用单数。
例如:Three weeks was allowed for making the necessary preparations.允许用三周的时间做必要的准备工作。
Ten yuan is enough.十元钱足够了。
1.5指代意义决定谓语的单复数
1) 集体名词作主语时,谓语的数要根据主语的意思来决定。如family, audience, crew, crowd, class, company, committee等词后用复数形式时,意为这个集体中的各个成员,用单数时表示该集体。
例如:His family isn’t very large.他家不是一个大家庭。
His family are music lovers. 他的家人都是音乐爱好者。
但集合名词people, police, cattle, poultry等在任何情况下都用复数形式。
例如:Are there any police around?周围有警察吗?
2)有些名词,如variety, number, population, proportion, majority 等有时看作单数,有时看作复数。
例如:A number of +名词复数+复数动词
The number of +名词复数+单数动词
例如:A number of books he lent out.不少书都被借出去了。
The majority of the students like English.大多数学生喜欢学英语。
1.6 与后接名词或代词保持一致
1) 用half of, part of, most of, a portion of 等词引起主语时,动词通常与of后面的名词,代词保持一致。
例如:Most of his money is spent on books.他的钱大多用来买书了。
Most of the students are taking an active part in sports.大部分学生都能积极参加体育活动。
2) 在一些短语,如 many a 或 more than one 所修饰的词作主语时,谓语动词多用单数形式。但由more than… of 作主语时,动词应与其后的名词或代词保持一致。
例如:Many a person has read the novel. 许多人都读过这本书。
More than 60 percent of the students are from the city.百分之六十多的学生都来自这个城市。
2.名词和代词一致
2.1 代词与其代替或修饰的名词在人称和性别上必须保持一致。
例如:(错误) Those of us who are over fifty years old should get their blood pressure checked regularly.
(正确) Those of us who are over fifty years old should get our blood pressure checked regularly.
我们中五十岁以上的人应该定期地检查血压。
3.同等成分一致
3.1句子中的同等成分应该在结构上保持一致,否则会失去平衡和协调。
例如:(错误)She is not only famous in China but also abroad.
(正确)She is famous not only in China but also abroad.
她不仅在中国,在国际上也很有名气。
3.2在比较结构中,被比较的事物应是同等成分。
例如:(错误)The workers in that factory are fewer than our factory.
(正确)The workers in that factory are fewer than those in our factory.
那个工厂的工人比我们厂的工人少。
代词、数词、介词、和连词
上面我们已经讲了动词、名词、形容词和副词的用法。中考中当然也会涉及到其他诸如代词、数词、介词、和连词等的用法。下面我就简单提醒大家每类词需注意的地方。
1.代词
同学们需掌握以下不定代词:all, each, both, either, neither, one, none, little, few, many, much, other, another, some, any, no以及由some, any, no, every构成的合成词如 nobody等,并注意不定代词的定语后置,如something English
2.数词
同学们需要记住一些特殊拼写的序数词。如:第1—— first 第2—— second 第3—— third 第5—— fifth 第9—— ninth第12—— twelfth 第20—— twentieth
另外需要记住以下短语:hundreds of 数以百计thousands of 数以千计tens of thousands of 数以万计several millions of好几百万 但表示确切的百或千时不能用复数形式,如:ten thousandthree million
3.介词
介词的考察内容主要是介词短语,特别是那些有固定搭配和固定用法的介词短语。这类短语比较多,这里我不再一一赘述,大家可以看《初中英语复习指导》第204页至208页上的词组。但我要特别提几个以前旧教材所没有的短语,请大家注意。
如,speak highly of高度赞扬 regard… as …视为,把……看做…… make a contribution to doing sth 为……做贡献
4.连词
同学们需要特别记忆以下连词或连词短语:neither…nor…either…or…not only…but also…both…and…前三个短语引导主语时,谓语动词需遵循就近原则。
如,Neither you nor I am right. 你和我都不正确。
Either Lucy or Lily is going there. 不是Lucy就是Lily要去那儿。
那么both…and…连接主语时,谓语动词要用复数形式。
如,Both Lucy and Lily are going there.
句子的种类
1.应特别注意掌握的简单句
有介词的特殊疑问句
在特殊问句中,作为介词宾语的疑问代词可以与介词分离,放在句首,而把介词放在句尾。
如,Whom do you trel with?当然,也可以把介词放在句首。
总之,不要把介词丢掉。
有插入语的特殊疑问句
在特殊问句中,经常可以看到这样的句子:Where do you think they may go?其中,do you think 是疑问式插入语,其余部分是think的宾语从句。注意,疑问式插入语同句子的其余部分不用逗号分开。
疑问式插入语还有do you hope, do you guess 等。在肯定句中也有插入语。如:That man, I guess, is neither a policeman nor a soldier. 在肯定句的插入语要用逗号与句子的其他部分分开。去掉插入语,该句子仍然是个完整的句子。
You’d better (not)… (do sth.) 这个说法常用于提出“劝告,建议,告戒”。 比较委婉的有礼貌的说法是 Would you like …? 或 What about (doing)…?如,It’s too dark. You’d better lee at once. I’m afraid (that) … I’m afraid (that) I can’t go with you today. 常用来委婉地表示自己的看法或预料一件令人不悦的事情。
2.并列句
并列句的考查重点是并列连词。并列连词有and, or, but, both… and, neither… nor, either… or, not only… but also…等。
3.复合句
复合句考查的主要内容是宾语从句、状语从句和定语从句。
①宾语从句
宾语从句的考查要点是:时态的呼应、人称的一致、词序等。
A.宾语从句的连接词:宾语从句本身是叙述句是,用that 引导。He said (that) he would lee on March 12 next weeek.宾语从句本身是特殊疑问句时,用疑问词引导。 Do you know where we can find our teacher?宾语从句本身是一般疑问句时,用if 或whether引导。I don’t know if / whether he has done that.
B. 宾语从句与主句时态的呼应。主句谓语是现在时和将来时的时候,宾语从句的动词时态不受影响。如,It is said that the panda was sent to America last month.主句是过去时态,从句谓语要做适当调整:
a)由现在时调整为过去时。I didn’t know you were also here.
b)由将来时调整为过去将来时He said that he would go to Beijing the next week.
c)过去时态多数不受影响,但“一般过去时”常调整为“过去完成时”,尤其是从句中有before, since 一类的时间状语时,多调整为“过去完成时”如:She said she had worked at this school before her father came to this city.
②状语从句
状语从句有时间状语从句(常由when, while, before, after, until, as soon as等词引导)、地点状语从句(常有where 引导)、原因状语从句(常有because, since, as 引导,这三词所表达的语气由because到as逐渐减弱,由why提出的问题必须用because 来回答), 条件状语从句(常由if引导)、结果状语从句(常由such … that…, so…that…, so that等引导 )、让步状语从句(常由though, although引导)。
③定语从句
其考查内容主要是正确使用关系代词{who(指人)、that(指人或物)、which(指物)} , etc. 定语从句一般紧跟在修饰词的后面,如:She is the person who I want to see. 她就是我想见到的人。有时,为了使句子平衡,也可把定语从句与所修饰词分开。
同学们还记得这样一句话吗?Then a screen came up that read,“Congratulations!” 这是第三册第54课中的一个句子。
Tomorrow (时间状语)they(主语) will cilmb over (助动词will+动词词组构成谓语)a high mountain(宾语)
Nobby(主语) wants(谓语) to make friends with selfish people(原因状语,不定式表原因)
The boy(主语) (is strong enough to 主语补足语)carry(谓语) the hey box (宾语)by himself(宾补).
希望能帮到你。不明白hi我









